Development challenge for synthetic polymer fibers and tapes: improving toughness
Vol. 17., No.10., Pages 991-991, 2023
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2023.73
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2023.73
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT

RELATED ARTICLES
Sandra Paszkiewicz, Kamila Sałasińska, Zaida Ortega, Mateusz Barczewski, Jacek Andrzejewski, Konrad Walkowiak, Izabela Irska, Magdalena Jurczyk Kowalska, Anna Boczkowska, Marcin Borowicz, Joanna Paciorek-Sadowska, Elżbieta Piesowicz, Katarzyna Pokwicka-Croucher
Vol. 19., No.12., Pages 1286-1309, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.95
Vol. 19., No.12., Pages 1286-1309, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.95
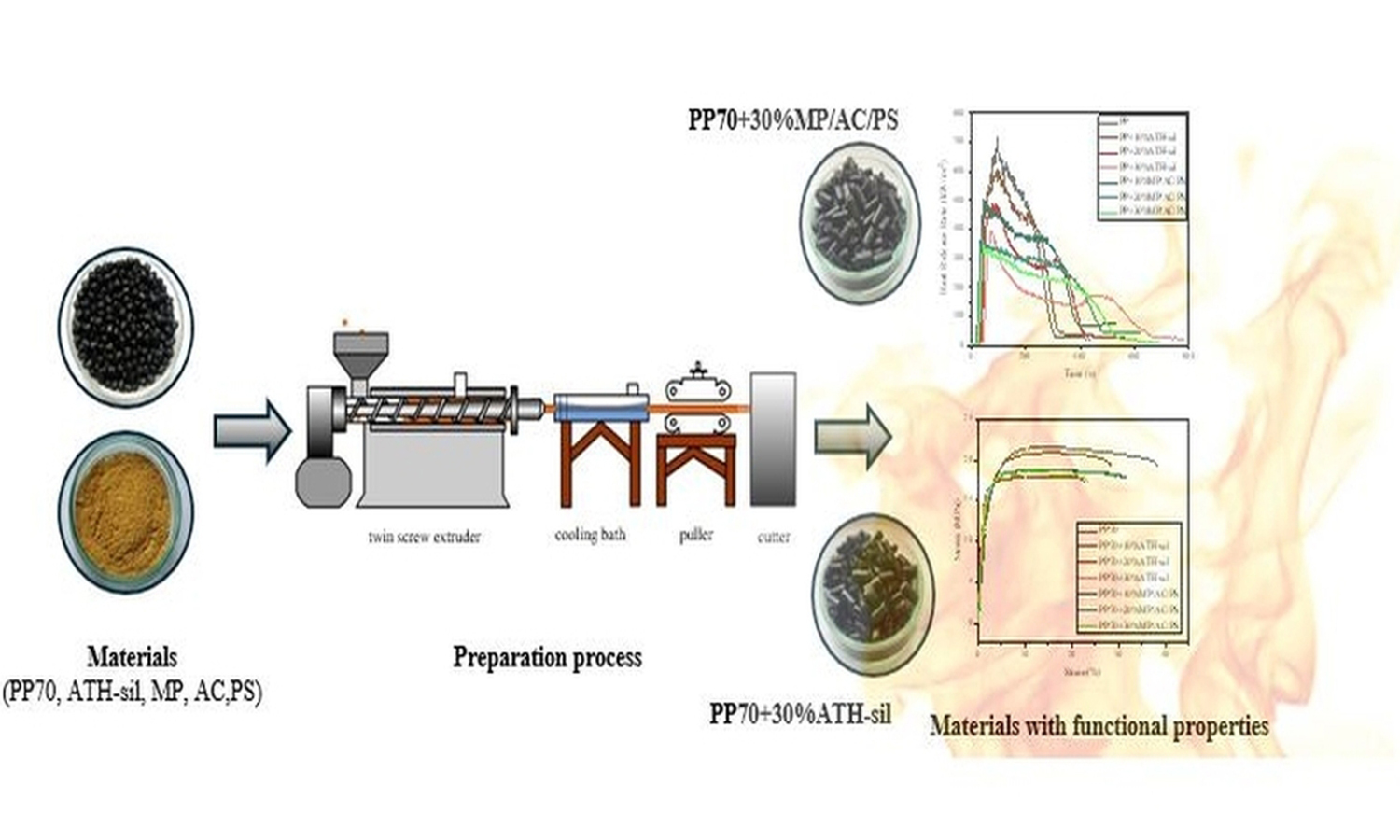
Two series of polymer blends based on post-consumer polypropylene (rPP) and tire rubber crumbs (Trc) under the trademark ECOPLASTOMER® PP70 with a mutual ratio of components 70/30 wt%, containing 10, 20, and 30 wt% of flame retardants, have been prepared using a twin-screw extruder. The influence of commercially available silane-treated alumina trihydrate (ATH-sil) with the eco-friendly system based on melamine phosphate (MP), aluminum hydroxide (AC), and peanut shells (PS), used as flame retardant agents, on the mechanical, thermal, and flammability properties of polymer blends was assessed – the incorporation of ATH-sil results in the appearance of peaks related to OH groups in the Fouriertransform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) spectra. Similar observations are made for the MP/AC/PS system. differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) analysis revealed that using the selected flame retardants did not impact the melting and crystallization temperatures of the polymer. Tensile strength experienced a minor decrease, particularly in compositions containing more than 20 wt% of the flame retardants, while hardness remained unaffected by their share. Both flame retardants reduced the flammability of the modified polypropylene/rubber powder blends, and the most favorable outcomes were achieved with ATH-sil; however, only when employed at a minimum of 30 wt%. The formulated MP/AC/PS system proved more adept at reducing flammability and smoke emissions at lower flame retardant levels (up to 20 wt%).
Jordi Puiggalí
Vol. 19., No.12., Pages 1214-1215, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.89
Vol. 19., No.12., Pages 1214-1215, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.89

This is an editorial article. It has no abstract.
Alexandra Maria Cardona Loaiza, Maria Eduarda Araújo Ribeiro, Ruben J. Sanchez Rodriguez
Vol. 19., No.9., Pages 862-877, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.66
Vol. 19., No.9., Pages 862-877, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.66
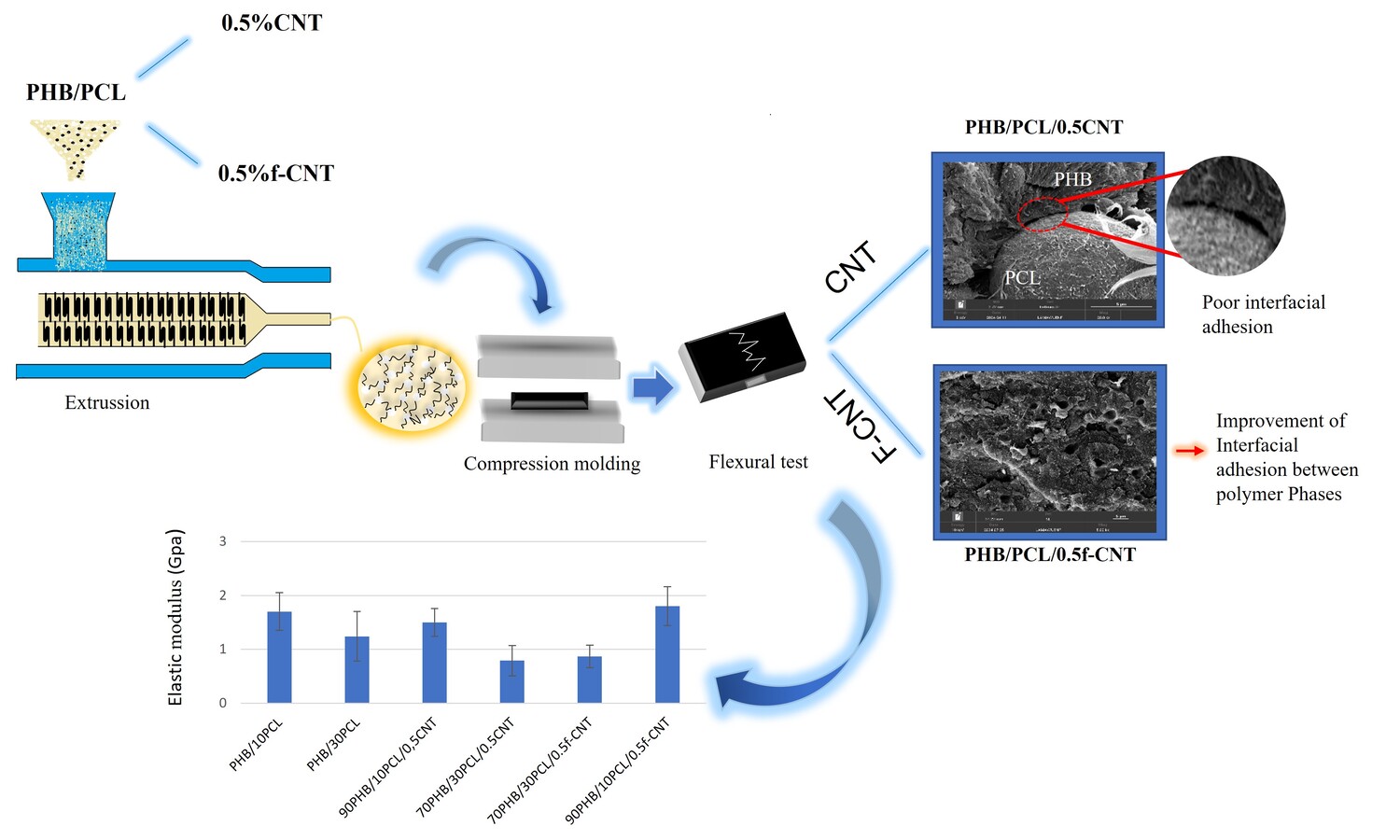
Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) is a polymer with great application potential; however, its brittleness and low mechanical strength restrict its use in many fields. This study investigated a strategy to overcome the mechanical limitations of PHB by blending it with polycaprolactone (PCL) and producing nanocomposites with non-functionalized carbon nanotubes (CNT) and functionalized ones (f-CNT). The effect of blend composition and the addition of f-CNT were studied in hotpressed specimens. In PHB/30PCL blends, a reduction in the overall crystallinity degree was observed, while in PHB/10PCL the crystallinity maintained close to neat PHB. In PHB/10PCL nanocomposites, no significant change was registered, but in PHB/30PCL with f-CNT, the crystallinity degree increased and achieved values comparable to PHB. Differential scanning calorimetry suggested that f-CNT had a higher impact in PCL crystallinity in formulations of PHB/30PCL. Scanning electron microscopy showed that in these formulations, f-CNT were preferably located at the interface of PHB/PCL, while in PHB/10PCL the particles were mainly located in PHB. In general, the blends suffered with a reduction in elastic modulus and strength, especially for PHB/30PCL formulation.
Quentin Watel, Aurélie Cayla, Fabien Salaün, François Boussu
Vol. 19., No.5., Pages 494-503, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.36
Vol. 19., No.5., Pages 494-503, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.36
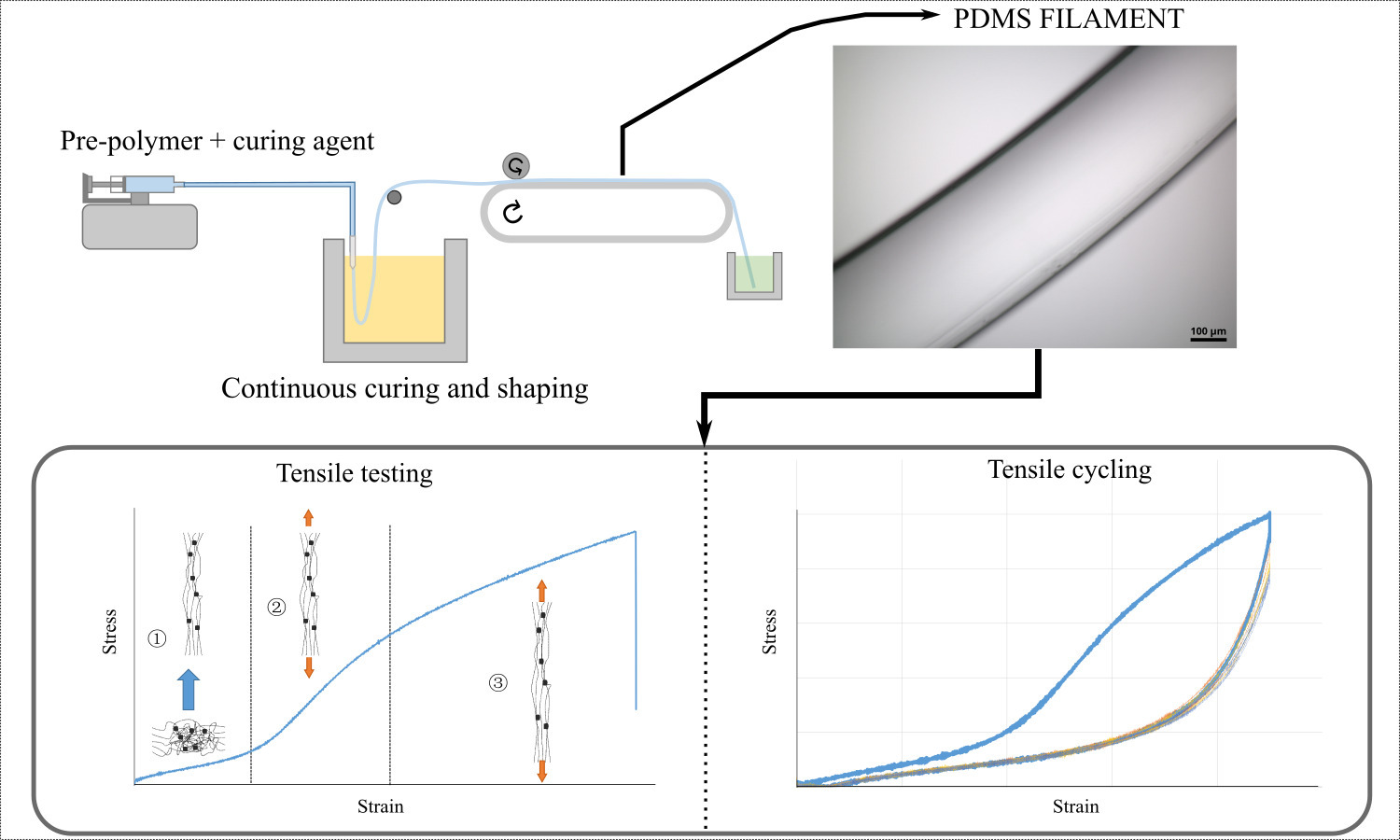
In this work, a PDMS spinning technique is developed and enables the continuous production of a filament with a circular cross-section (~500 μm diameter). The production of continuous silicone polymer filaments can be useful in the textile field to provide new properties in applications such as weaving, knitting or composite reinforcement. The method involves injecting the pre-polymer and curing agent mixture into a heated oil bath (202–215 °C) to simultaneously shape and cure the PDMS. The morphological and mechanical properties of the filament are studied regarding the production parameters (formulation, needle diameter, bath temperature, conveyor belt speed). The most homogeneous filament is produced at the highest temperature (215°C) and conveyor belt speed (13.6 m∙min–1). When subjected to cyclic mechanical stress, the PDMS filament produced exhibits stable mechanical behavior, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Mohammad Mehdi Alighanbari, Firoozeh Danafar, Araam Namjoo, Asma Saeed
Vol. 19., No.1., Pages 15-46, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.3
Vol. 19., No.1., Pages 15-46, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.3
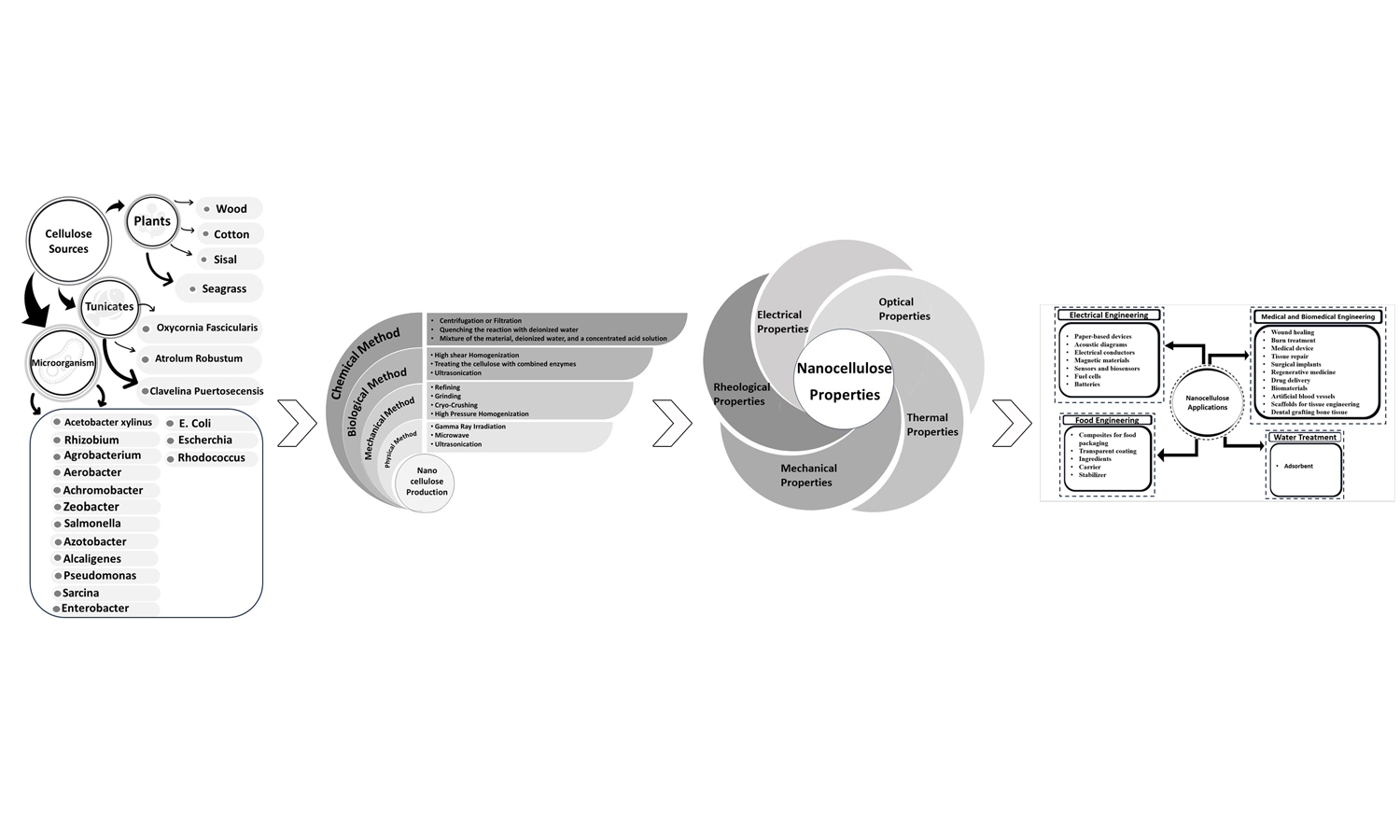
The environmental and ecological concerns drive researchers to synthesize functional materials using components from natural resources. Nanocellulose (NC), derived from plants, marine animals, or microorganisms, is a green material attracting attention due to its abundance, biocompatibility, and biodegradability. NC’s interstice properties enable the synthesis of functional nanocomposites in forms like aerogels, foams, paper, sheets, or hollow filaments. This review briefly describes NC classification and production while comprehensively presenting its mechanical, rheological, optical, and electrical properties, offering foundational knowledge for future research. Additionally, it highlights recent developments in NC-based products across fields such as papermaking, water treatment, civil engineering, electronics, cosmetics, food, and medicine. For the first time, this paper explores recent advances in NC molecular simulation, providing insights into structure, arrangement, and interactions through molecular dynamic simulation. Finally, future prospects for NC-based applications are discussed to encourage studies addressing current challenges.




