Poly(vinyl propionate)-grafted natural rubber as a compatibilizer in vulcanized blends of natural rubber and butadiene-crylonitrile rubber: Effects on morphology, thermal and mechanical properties
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 186-196, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.15
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.15
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT

ABSTRACT
Natural rubber (NR) and acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) are typically incompatible due to differences in their polarity, which causes poor mechanical properties. In this study, a new type of compatibilizer, namely G10 or poly(vinyl propionate)-grafted natural rubber (NR-g-PVP) containing 10 wt% PVP, is employed to improve the compatibility in 50/50 blends of NR and NBR. The results show that G10 promotes the compatibility and shifts the glass transition temperatures (Tg) of NR and NBR towards each other. This indicates that G10 interacts with both NR and NBR phases. The improved compatibility resulted in a more homogeneous blend with smooth surface morphology. The mechanical properties of the blend, including 300 and 500% moduli, tensile strength, and tear resistance, increased with G10 content up to 7.5 phr. The highest tensile strength of the NR/NBR blend was achieved with 7.5 phr of G10 compatibilizer, showing an improvement of approximately 40.7% over the control sample. The results clearly revealed that NR-g-PVP can be utilized as an effective compatibilizer in NR/NBR blends.
RELATED ARTICLES
Paulina Wiśniewska, Natalia A. Wójcik, Józef Haponiuk, Jacek Ryl, Henri Vahabi, Krzysztof Formela, Mohammad Reza Saeb
Vol. 19., No.9., Pages 878-892, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.67
Vol. 19., No.9., Pages 878-892, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.67
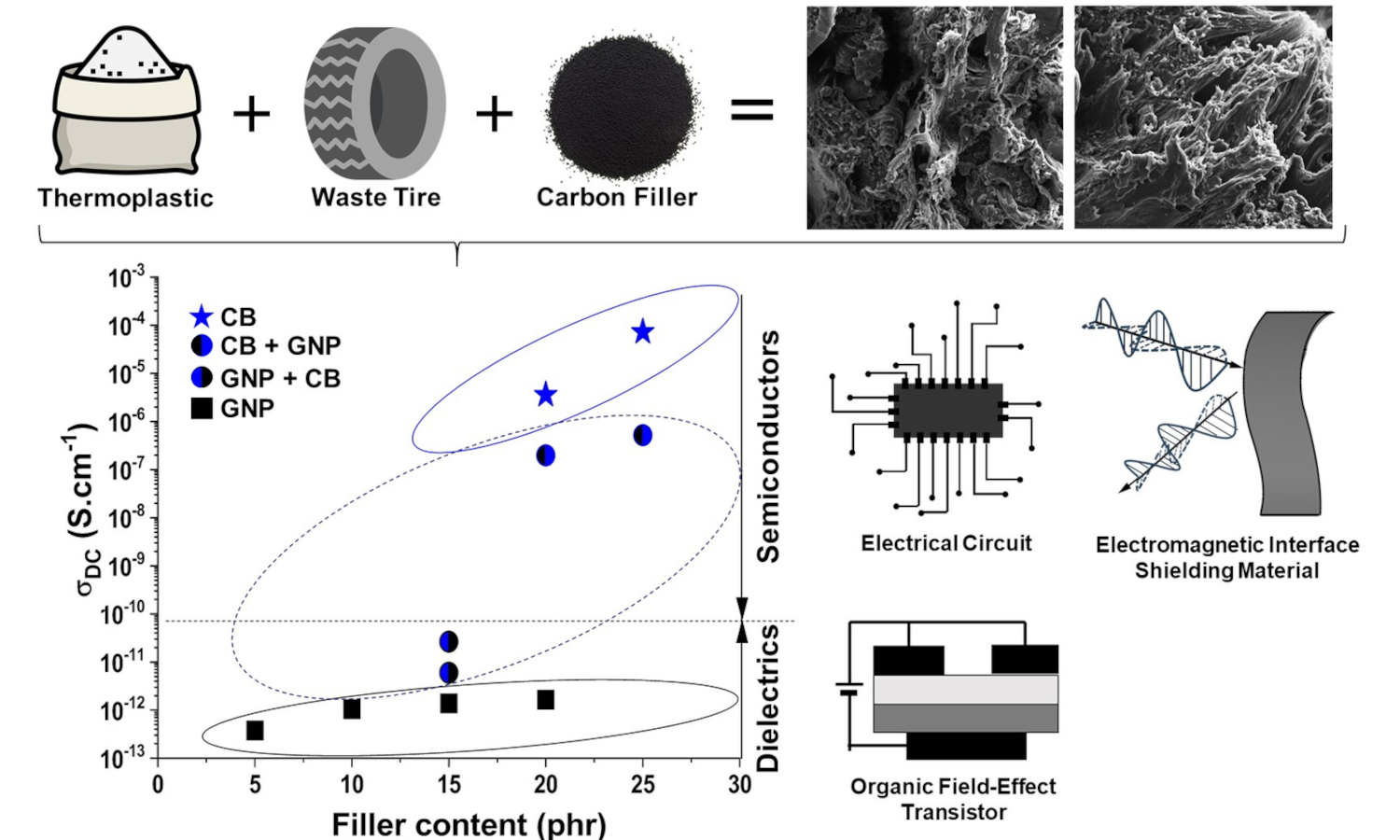
Waste rubber management through developing blends of thermoplastics with ground tire rubber (GTR) has gained significant attention for creating sustainable, high-performance materials with enhanced properties. In this work, we developed customized graphene/polymer nanocomposites applying GTR, ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA), and graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs), taking carbon black (CB) as the reference additive. A wide range of electrical conductivity from 10–12 S/cm (dielectric) to 10–5 S/cm (semiconductor) was obtained for optimized composites containing GNPs and CB, respectively. Thermal, mechanical, and flame-retardant properties looked promising for additive manufacturing, while electrical conductivity was tailored for soft electronics. In view of processability, mechanical strength, and elasticity, GNPs-incorporated EVA/GTR composites showed an edge over their CB-aided counterparts. For example, tensile strength and elongation at break of EVA/GTR blends reinforced with 20 phr GNPs were 4.8 MPa and 681%, respectively, compared to 4.0 MPa and 651% for the composite comprising an identical amount of CB. Interestingly, combining GNPs and CB enhanced the thermal stability and flame retardancy of EVA/GTR compared to only GNPs or CB. These results were promising from both sustainability and advanced functional materials perspectives.




