Influence of thermal degradation on the crystallization of poly(butylene terephthalate)
Vol. 18., No.3., Pages 309-325, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.22
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.22
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
Our work reveals a notable shift in the crystallization temperature (Tc) of poly(butylene terephthalate) (PBT) at which crystallization occurs due to exposure to prolonged thermal degradation at 270°C in an environment of nitrogen gas. The initial Tc of 193°C undergoes a marked decrease, settling at 133°C, which signifies a considerable 60°C shift towards lower temperature ranges. This transition is discernible across three distinct degradation stages: an initial phase of increase, an intermediate phase characterized by a sharp decline, and a subsequent late stage of the degradation phase characterized by a more moderate decrease in Tc. Both crystallinity and crystallization kinetics consistently mirror this pattern, demonstrating an initial rise, a rapid subsequent drop, and a gradual decline in the late-stage period. Evident from the presence of two melting peaks, the research implies differing lamellar thicknesses. As the degradation progresses, the melting points of these peaks, denoted as Tm1 and Tm2, decline at 38 and 41°C, respectively. Validation of the degradation-induced changes is provided by a small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS), which corroborates the observed decrease in the long period (L). A contextualization of the results against prior studies underscores analogous trends in the alteration of crystallization behaviour consequent to degradation.
RELATED ARTICLES
Evangelia Balla, Panagiotis Klonos, Apostolos Kyritsis, Dimitrios Bikiaris
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 154-167, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.13
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 154-167, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.13
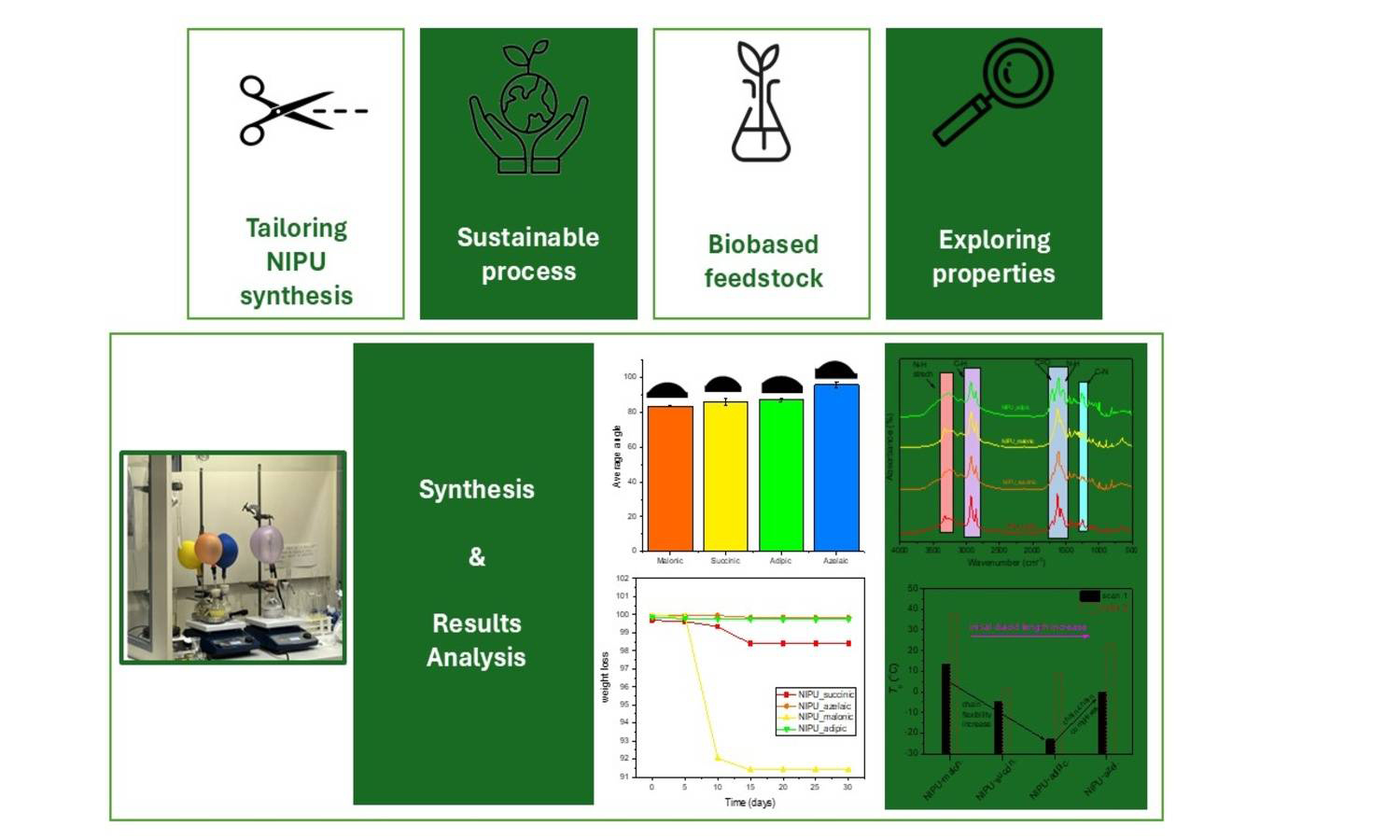
In recent decades, numerous efforts have been dedicated to the investigation of eco-friendly non-isocyanate polyurethanes (NIPUs) as alternatives to conventional polyurethanes (PUs). Since isocyanates are classified by the EU as hazardous and toxic compounds, NIPUs offer a promising route to mitigate isocyanate-related health risks as well as other environmental concerns associated with traditional PU synthesis. In the present study, we report the synthesis as well as the detailed structural and thermal characterization of a new series of fully biobased non-isocyanate polyurethanes (NIPUs) based on aliphatic dicarboxylic acids of different chain lengths. The NIPUs were prepared via a two-step polyaddition reaction involving glycerol carbonate and diamine. Their synthesis enables a sustainable pathway to tailor NIPUs’ physicochemical properties via diacid structure control. Studies of their structure, thermal behavior and trends, morphological, and hydrolytic findings confirmed strong diacid chain length dependence on glass transition temperature (Tg ~13, 0, ‒5 and –23 °C), molecular weight, surface wettability, and enzymatic degradability. Short-chain diacids yielded NIPUs with rapid hydrolytic degradation, while their longer-chain analogs were hydrophobic and thermally stable. Contact angle measurements (~75–85°) also confirm these trends. The tunable properties position these materials among strong candidates for biomedical applications.
Isabel Milagros Gavilan-Figari
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 72-81, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.6
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 72-81, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.6
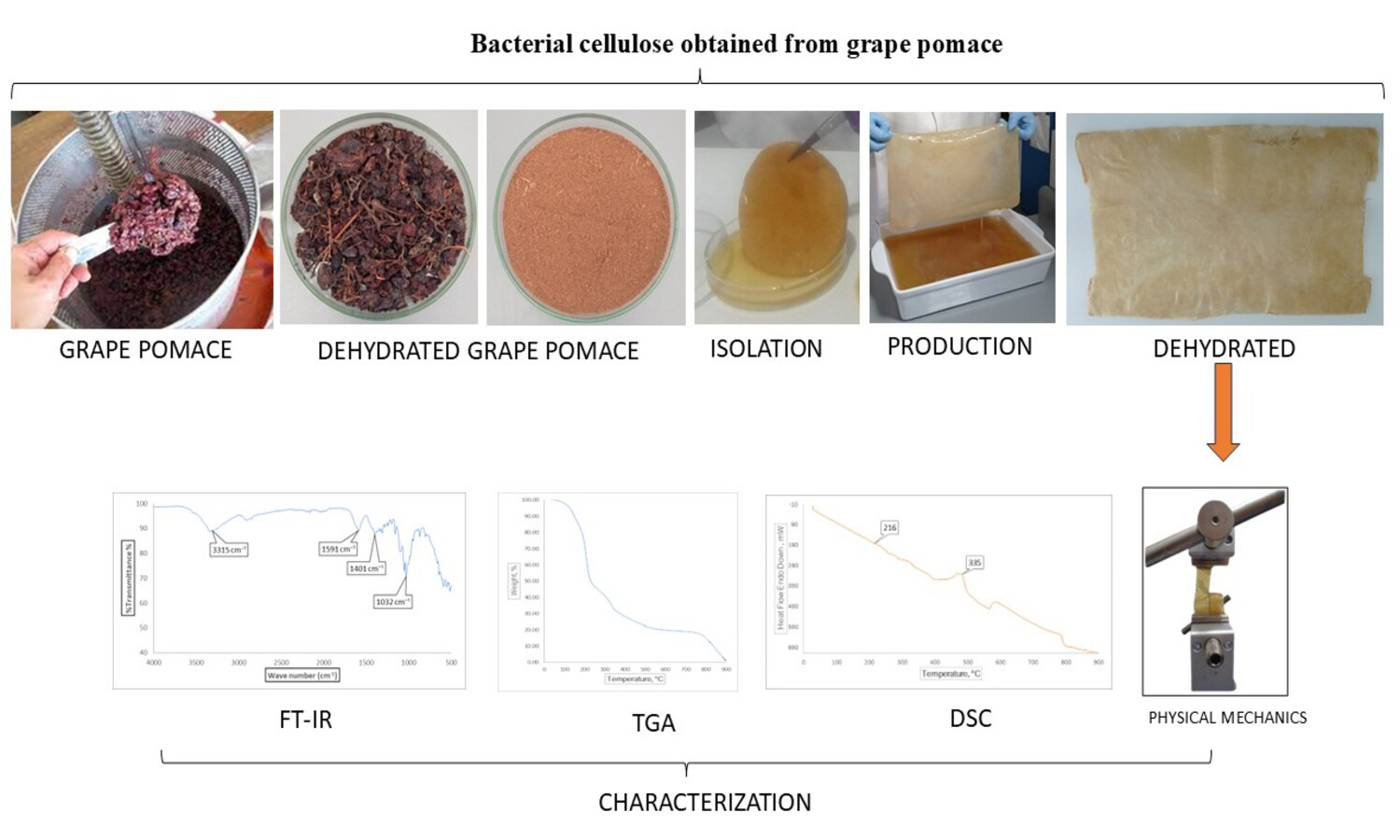
Bacterial cellulose (BC) is an eco-friendly biopolymer with outstanding structural and functional properties, offering promising applications in sustainable packaging and bio-based materials. In this study, we demonstrate the feasibility of producing BC via spontaneous fermentation, using grape pomace supplemented with sucrose as the sole carbon source, nutrient substrate, and microbial inoculum, without the addition of commercial strains or nitrogen supplements. Fermentation was conducted under static conditions, yielding biofilms with stable structural characteristics and BC production of up to 14.1 g/L, thereby confirming the efficiency of this low-cost, residue-based process. The films obtained exhibited well-organized polymeric networks, with thermal stability in the range of Tg ≈ 159–266 °C and mechanical resistance comparable to or higher than conventional biopolymers. Characterization confirmed reproducible chemical profiles, thermal stability, and measurable variation in mechanical performance, with a tensile strength ranging from 0.0001 to 105 MPa and an elongation at break of 15±5%. The process highlights a resource-efficient and sustainable pathway, adaptable to rural contexts and aligned with circular economic principles. While minor variations among replicates reflected the intrinsic variability of biological systems, mean values and standard deviations demonstrated reproducible physicochemical and mechanical properties. These findings demonstrate that BC derived from agro-industrial residues can be produced under simple, low-input conditions, opening opportunities for scalable valorization in functional and sustainable materials.
Longqiang Xiao, Weijia Huang, Kaihong Lin, Shucui Han, Zuyun Luo, Linxi Hou, Yan’gen LV
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 3-17, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.2
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 3-17, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.2
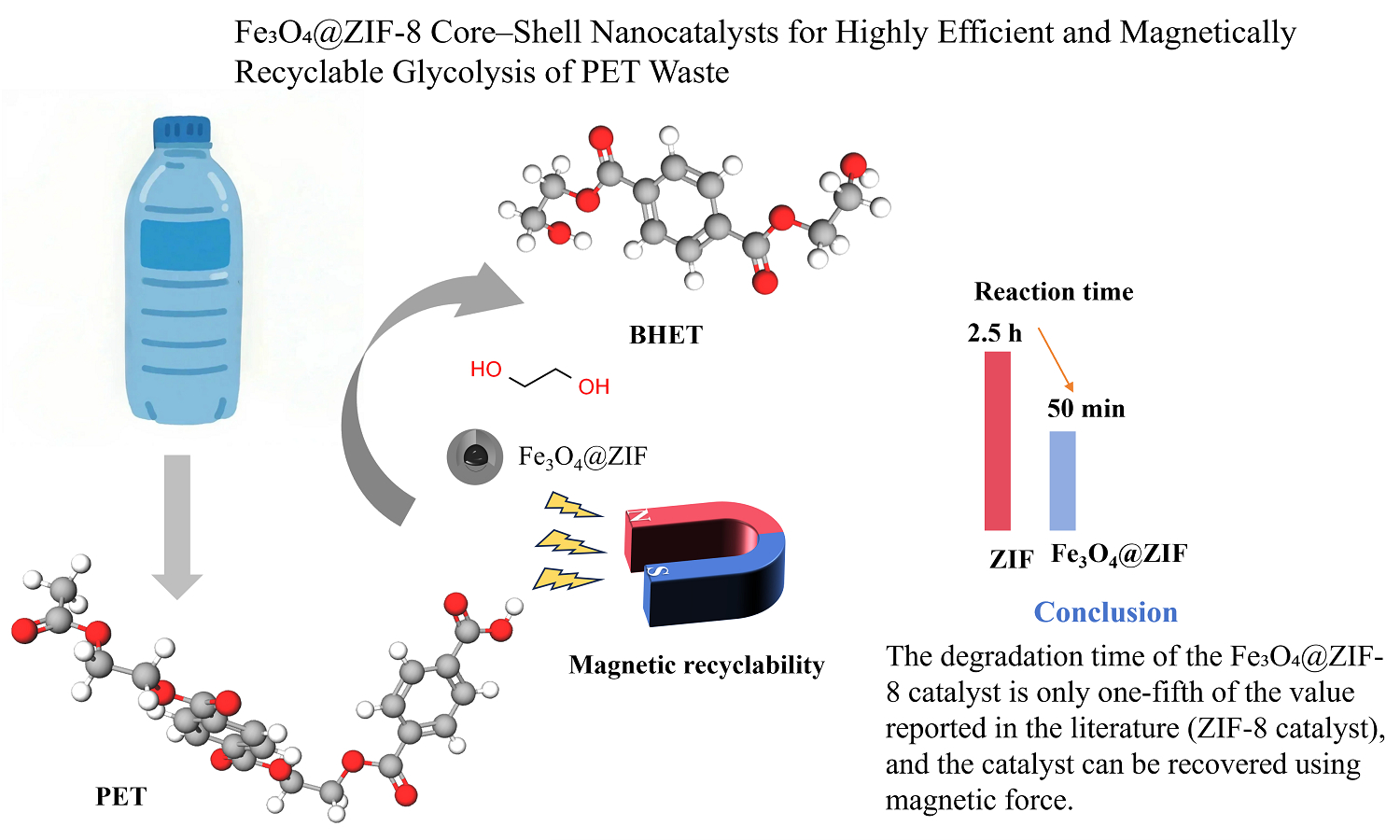
In this study, magnetic core-shell Fe3O4@ZIF-8 was synthesized via a hydrothermal method and applied to Polyethylene terephthalate(PET) degradation. The catalytic degradation of PET by Fe3O4@ZIF-8 was carried out under atmospheric pressure, yielding high-value bis(2-hydroxyethyl) terephthalate (BHET) monomers. The as-synthesized Fe3O4@ZIF-8 core-shell composites possess hierarchical porosity with tunable nanoscale cavities. SEM and TEM analyses confirmed the core-shell morphology, with nanoparticles having a size distribution of 180–280 nm. The degradation product was identified as a high-purity, colorless, and transparent monomeric BHET through 1H NMR and LC analyses. Based on a series of onefactor experiments and a Box-Behnken experimental design, the optimal process conditions were determined to be an alcoholysis temperature of 200°C, a catalyst dosage of 0.5 wt% (relative to PET mass), a reaction time of 50 min, and an ethylene glycol-to-PET mass ratio of 4.5:1. Under these conditions, the actual BHET yield reached 81.12%, closely matching the predicted value.




