Hemp extract as a multifunctional stabilizer for polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) materials: Investigations into anti-aging properties and lifetime control
Karol Tutek, Anna Masek
Vol. 19., No.1., Pages 107-121, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.8
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.8
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
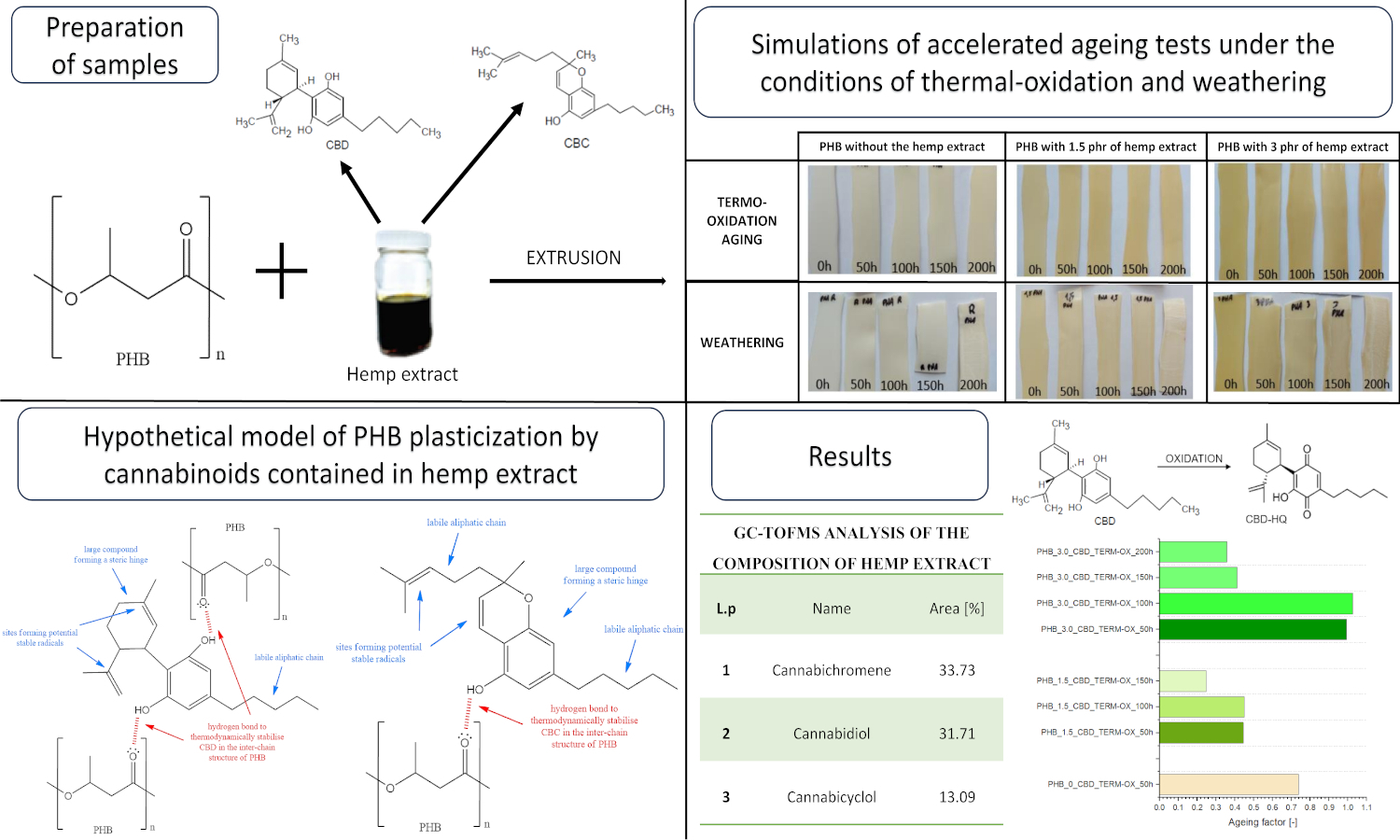
ABSTRACT
Biodegradable biopolymers like polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) hold promise for sustainable packaging, but their inherent degradability reduces material stability. Synthetic stabilizers, though effective, raise environmental and potential toxicity concerns. This study explores a multifunctional natural anti-aging agent: a hemp extract rich in cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabichromene (CBC). PHB composites with varying hemp extract concentrations were prepared and subjected to thermooxidative and weathering aging. Characterization employed FTIR-ATR, carbonyl index, and spectrophotometry. Static mechanical properties, DSC, and surface free energy (SFE) were also assessed. Notably, the hemp extract exhibited stability under ambient conditions but showed migration with time and aging. The results suggest a plasticizing effect on PHB and highlight the contrasting roles of the extract: inhibiting thermooxidative aging while potentially accelerating aging under atmospheric conditions. This opens avenues for tailoring material durability, further evaluated by life cycle analysis (LCA). This work represents one of the first investigations into hemp extract as an anti-aging agent for eco-friendly polymers, expanding the knowledge base of natural multifunctional additives.
RELATED ARTICLES
Cláudia Andréa Batista dos Santos, Bartłomiej Kryszak, Rafał Malinowski, Aleksandra Ujćič, Konrad Szustakiewicz
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 264-278, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.21
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 264-278, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.21

This study investigates the interaction between poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) and amber powdered waste (AbW) from jewelry at different filler concentrations (0, 1, 2.5, and 5 wt%) obtained via melt mixing in a corotating twin screw extruder. The resulting materials were pelletized and processed using two techniques: 1) cast film extrusion and 2) injection molding. The shaped specimens exhibited excellent interfacial adhesion. Thermal behavior, as assessed by Vicat softening temperature (VST), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), showed minimal variation among the composites. Despite similar melt flow rate (MFR) values among the samples, the incorporation of AbW affected the behavior of the polymer during cast film extrusion. Consequently, the composite films exhibited lower tensile mechanical parameters (tensile strength, Young’s modulus, stress and strain at break) compared to the neat PBAT film. In turn, the injection molded composites showed improved tensile, flexural, and impact parameters compared to their neat counterpart. Additionally, a slight decrease in water contact angle (WCA) suggested increased surface hydrophilicity of the extruded films. These findings demonstrate the potential of AbW as an additive for biopolymer composites with enhanced mechanical performance. The increased surface hydrophilicity is particularly relevant for applications targeting biocompatibility and biodegradability.
Effect of natural cinnamon extract on the stabilizing properties of biodegradable packaging polymers
Anna Kosmalska-Olańska, Anna Masek
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 52-71, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.5
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 52-71, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.5

The growing focus on sustainability, eco-friendly technologies, decarbonization, and reducing carbon footprints shapes current industry challenges. This article reviews the potential of cinnamon as a bio-additive for polymer stabilization in packaging. Samples were prepared from ethylene-norbornene copolymer (Topas), a cyclic olefin copolymer known for purity, transparency, and low gas permeability, and poly(lactic acid) (PLA), a bio-based alternative to petroleum plastics. Cinnamon powder was added in 0.5, 1.0, and 1.5 wt%. After solar and thermo-oxidative aging, hydrophobicity, chemical composition, mechanical, and color properties were analyzed. Results showed higher hydrophobicity and resistance to hydrolytic degradation due to reduced water penetration. PLA, normally brittle, became more flexible, with 0.5 wt% cinnamon showing optimal performance after 100 h of solar aging, similar to Topas composites. Overall, PLA and cyclic olefin copolymer (COC) films with cinnamon improved durability, extended food shelf life, and acted as natural color indicators of material aging.
Yashpal Singh, Raj Kumar, Nikhil Chauhan, Tejas Pramod Naik, Inderdeep Singh
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 97-111, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.8
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 97-111, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.8
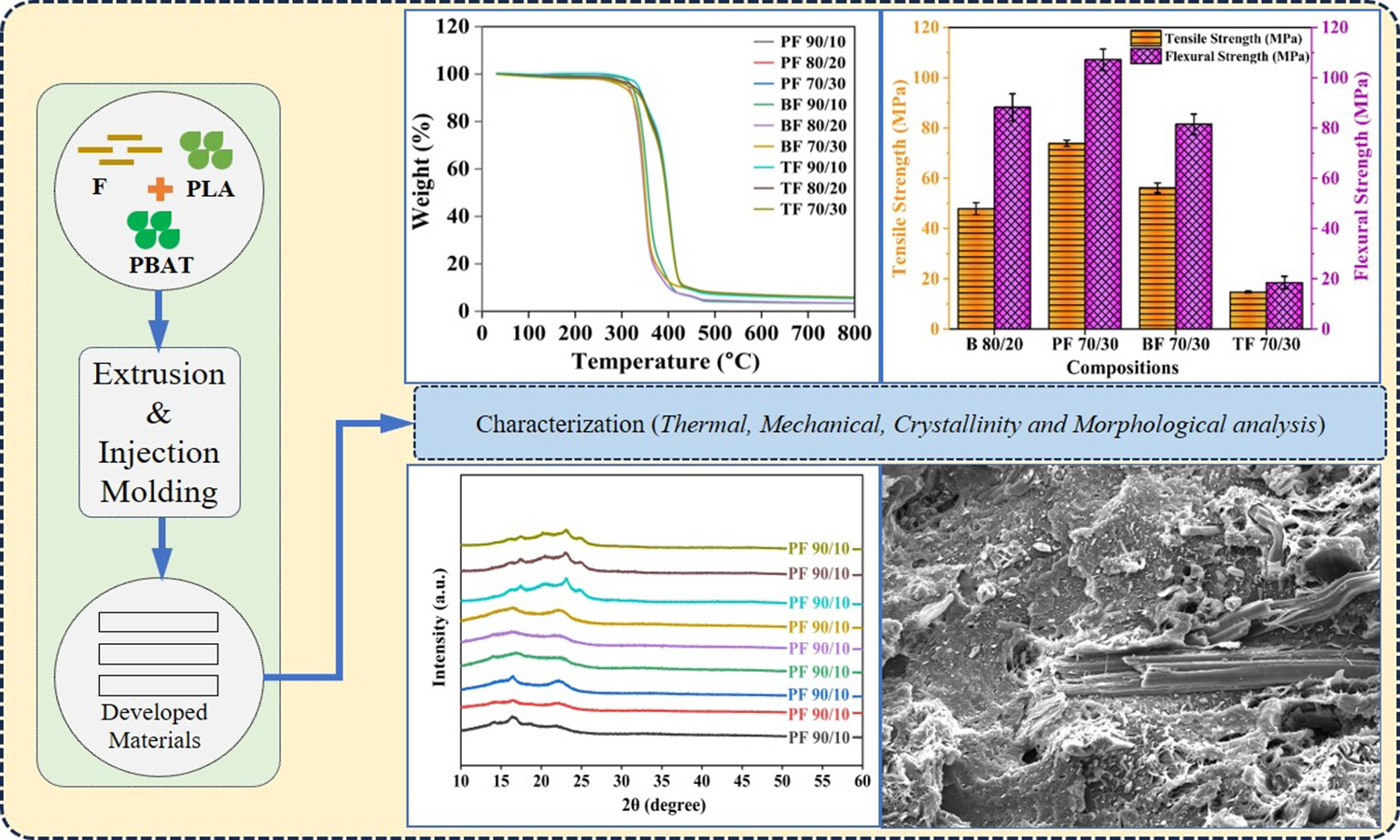
The current experimental investigation presents a comparative evaluation of selected biodegradable polymer blends and their composites, focusing on their material properties. Two biopolymers, polylactic acid (PLA) and polybutylene adipate-co-terephthalate (PBAT), along with pineapple fibers (F), as bio-reinforcement were taken for the analysis, which was conducted in two stages: During first stage, PBAT was melt-blended with PLA in varying weight fractions (10, 20, 30, 40, and 50 wt%) to produce PLA/PBAT blend (B) and in second stage, PLA, PBAT, B 80/20 blend were reinforced with pineapple fiber (10, 20, and 30 wt%). The samples were fabricated using extrusion-injection molding. The samples were characterized for density, thermal degradation, crystallinity, and mechanical behaviour. Among the blends, the optimal B 80/20 combination exhibited tensile strength, flexural strength, and elongation at break of 47.9±2.4, 88.2±5.4 MPa, and 330.6±10.47%, respectively. Results indicate that the PLA-based composites (PF) exhibit significantly better density, tensile strength, and flexural strength as compared to neat polymers, blends, blend-based composites (BF), and PBAT-based composites (TF). Among the PF composites, the PF 70/30 composite demonstrated superior performance, with maximum tensile and flexural strength values of 73.9±1.3 and 107.1±4.3 MPa, respectively.
Guilherme Ribeiro de Carvalho, Rafael Affonso Netto, Camila Delarmelina, Marta Cristina Teixeira Duarte, Liliane Maria Ferrareso Lona
Vol. 19., No.7., Pages 686-696, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.52
Vol. 19., No.7., Pages 686-696, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.52
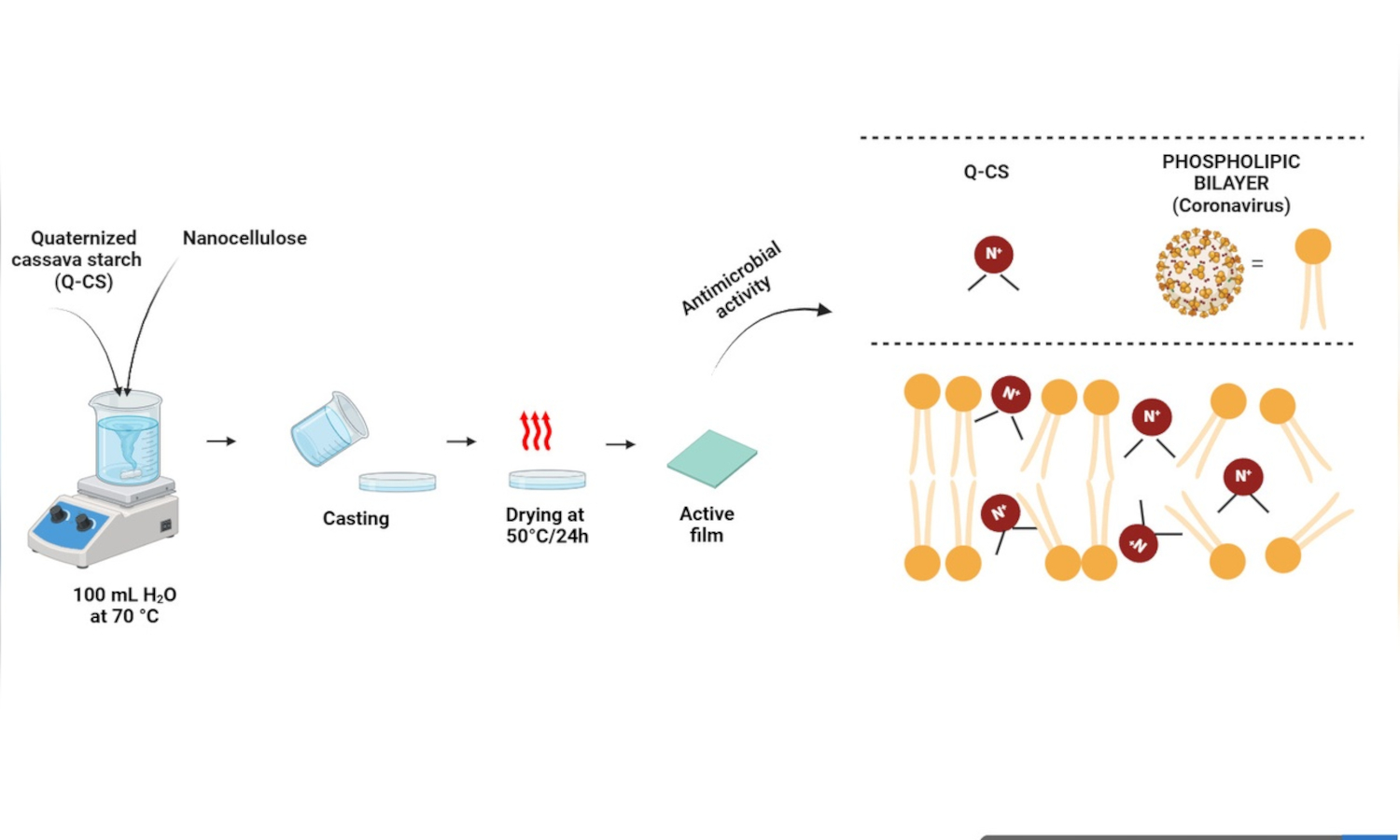
In this study, a new plastic film with antiviral and antibacterial properties was developed using modified cassava starch with glycidyltrimethylammonium chloride (GTMAC) and reinforced by crystalline nanocellulose (CNC), called Q-CS/CNC. For comparison, a control film (Q-CS) was produced without the addition of CNC. Elemental analysis revealed a degree of substitution (DS) of 0.552, indicating the replacement of the OH groups of starch by the NR4+ groups of GTMAC during the quaternization reaction. The addition of CNC resulted in significant increases (p < 0.05) of 38.9, 38.2, and 43.1% in thickness, opacity, and water vapor permeability measurements, respectively, compared to Q-CS. Incorporating CNC also contributed to an increase of 43.6% in tensile strength and 109% in stiffness but slightly decreased thermal stability. The Q-CS/CNC film demonstrated efficacy by inactivating 99% of the coronavirus in 1 min and inhibiting the growth of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. This action is attributed to the electrostatic interaction of quaternary amino groups, grafted onto starch, with the phospholipid membrane of microorganisms, resulting in the inactivation of these microorganisms. Therefore, these results highlight the potential use of Q-CS/CNC film as antimicrobial packaging, especially against coronavirus.
Lilla Bubenkó, Násfa Németh, Sára Frey, Tamás Molnár, Károly Belina, Orsolya Viktória Semperger
Vol. 19., No.7., Pages 726-735, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.55
Vol. 19., No.7., Pages 726-735, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.55
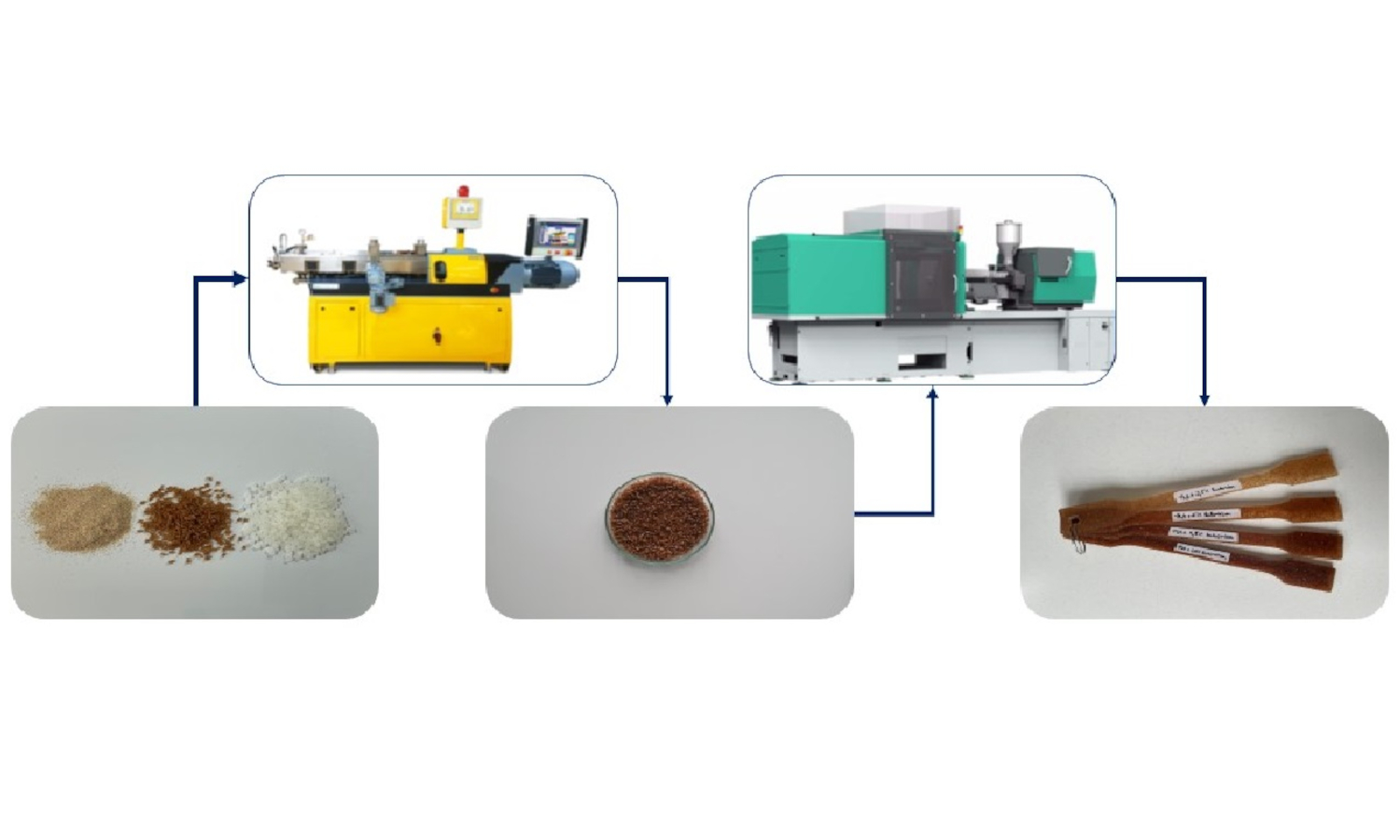
Biocomposites have recently received more attention because of raising environmental awareness and the drive toward sustainable technologies. The most common biodegradable polymer is poly(lactic acid) (PLA), which has an excellent balance of physical and rheological properties, but there is some limit to its usage. PLA properties can be improved by adding different types of fibers or fillers that come from agricultural waste. In this study, corn cob and lavender stem were used to reinforce PLA without any coupling agent, and the properties of the composites were investigated. The melt flow rate (MFR) values decreased with the corn cob content and increased with the addition of lavender stem. Mechanical tests showed that the tensile and flexural modulus of the composites increased and the strengths decreased with the reinforcement material content. The rigidness of PLA slightly decreased with the addition of fillers. There was no significant effect on the thermal properties. The unremarkable improvement of the reinforcement was due to the lack of appropriate adhesion of the two phases. The structure of the compounds was found to be homogenous on the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) micrographs. The incorporation of corn cob and lavender stem can reduce the production cost of materials.



