General trends in highly cited articles in Express Polymer Letters
Vol. 18., No.1., Pages 1-1, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.1
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.1
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT

RELATED ARTICLES
Guilherme Ribeiro de Carvalho, Rafael Affonso Netto, Camila Delarmelina, Marta Cristina Teixeira Duarte, Liliane Maria Ferrareso Lona
Vol. 19., No.7., Pages 686-696, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.52
Vol. 19., No.7., Pages 686-696, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.52
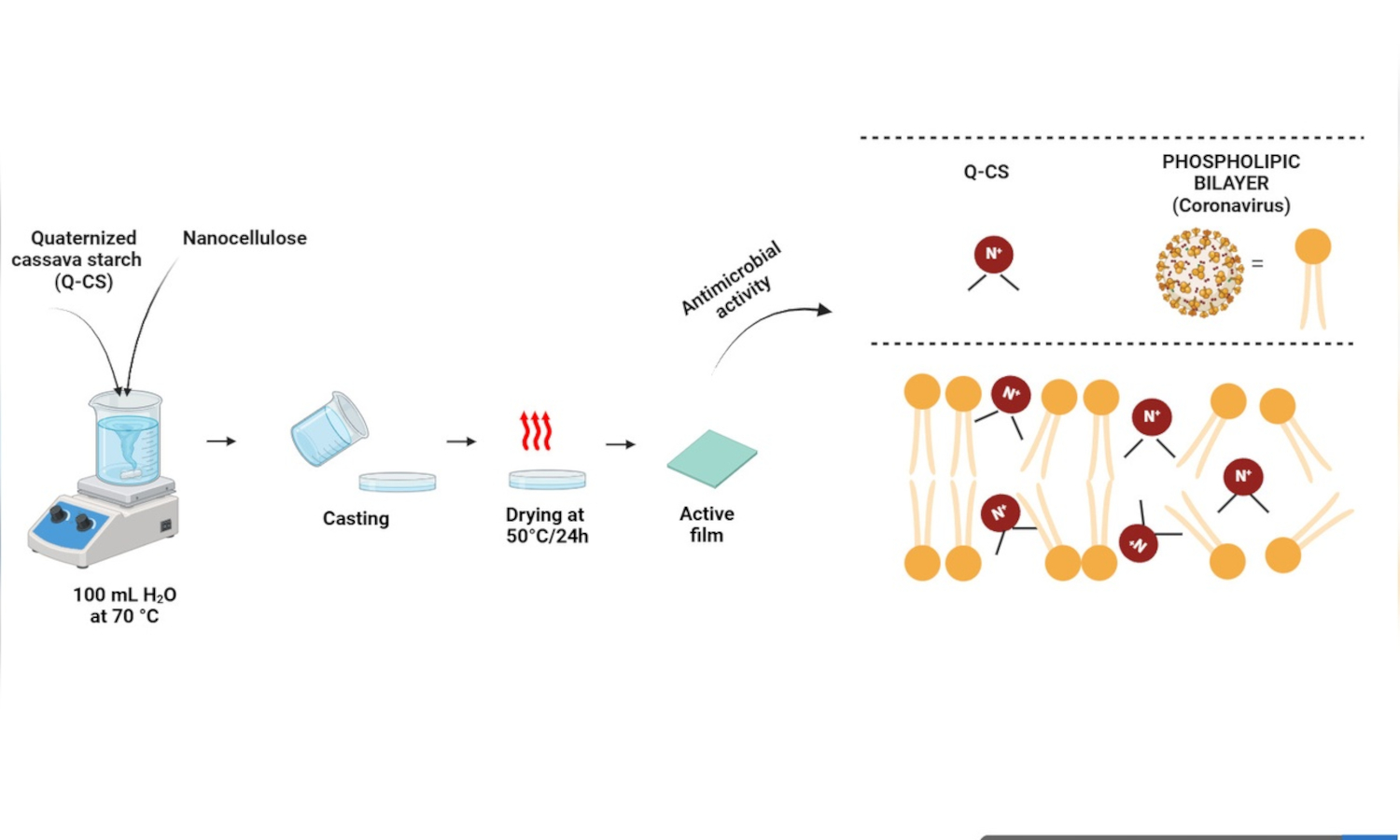
In this study, a new plastic film with antiviral and antibacterial properties was developed using modified cassava starch with glycidyltrimethylammonium chloride (GTMAC) and reinforced by crystalline nanocellulose (CNC), called Q-CS/CNC. For comparison, a control film (Q-CS) was produced without the addition of CNC. Elemental analysis revealed a degree of substitution (DS) of 0.552, indicating the replacement of the OH groups of starch by the NR4+ groups of GTMAC during the quaternization reaction. The addition of CNC resulted in significant increases (p < 0.05) of 38.9, 38.2, and 43.1% in thickness, opacity, and water vapor permeability measurements, respectively, compared to Q-CS. Incorporating CNC also contributed to an increase of 43.6% in tensile strength and 109% in stiffness but slightly decreased thermal stability. The Q-CS/CNC film demonstrated efficacy by inactivating 99% of the coronavirus in 1 min and inhibiting the growth of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. This action is attributed to the electrostatic interaction of quaternary amino groups, grafted onto starch, with the phospholipid membrane of microorganisms, resulting in the inactivation of these microorganisms. Therefore, these results highlight the potential use of Q-CS/CNC film as antimicrobial packaging, especially against coronavirus.
Seisuke Ata, Takumi Ono, Motonari Shibakami
Vol. 19., No.6., Pages 628-635, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.47
Vol. 19., No.6., Pages 628-635, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.47
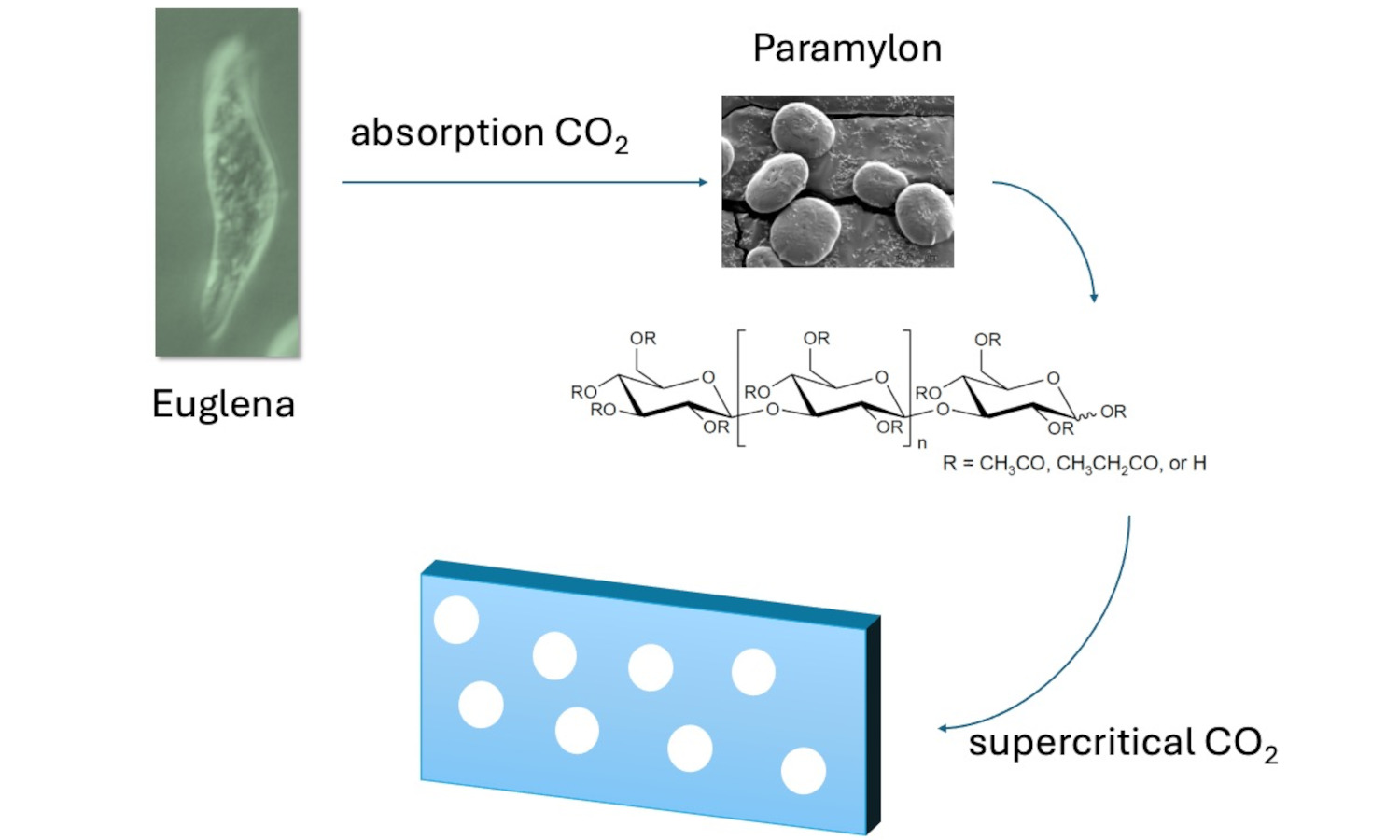
This study demonstrated, for the first time, the successful formation of porous paramylon esters, which were made from euglenoid polysaccharide known as paramylon and short-chain fatty acids, through supercritical CO2 processing. By maintaining a constant ester functional group attached to the paramylon and varying its proportion, distinct porous structures were selectively produced. Solubility parameter estimations indicated that changes in esterification had no significant effect on the solubility of the paramylon esters used in the experiment. Thus, these structural differences are likely attributed to variations in the viscoelastic properties of paramylon esters under supercritical CO2 conditions. Furthermore, thermal conductivity measurements revealed reductions of up to 20%. Intriguingly, substantial decreases in thermal conductivity were observed even at low foaming ratios, achieved through precise control of the porous structure.
Konrad Stefaniak, Anna Masek
Vol. 19., No.4., Pages 386-408, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.29
Vol. 19., No.4., Pages 386-408, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.29
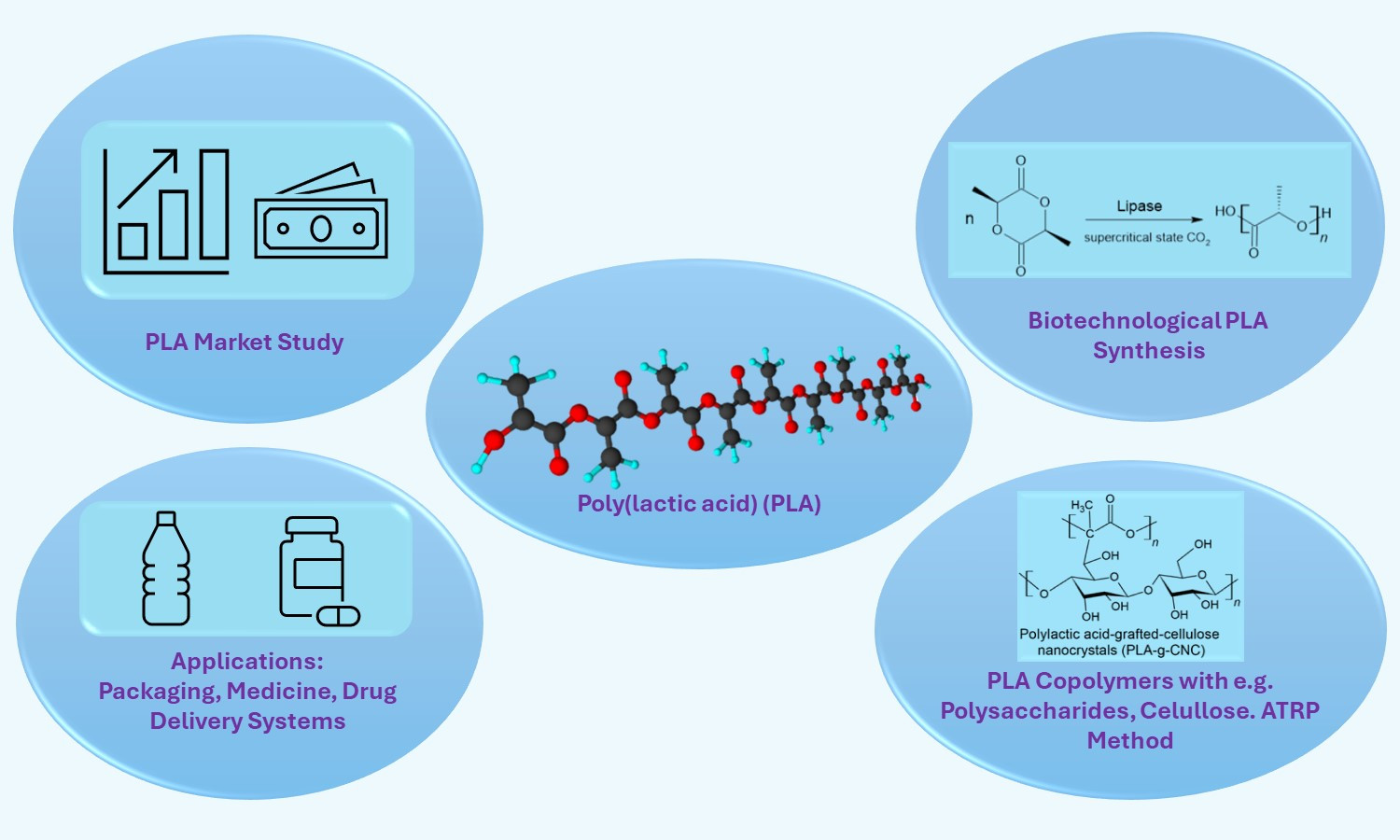
This review is focused on recent achievements in poly(lactic acid) (PLA) synthesis and copolymerization with special regard to biotechnological routes of PLA synthesis, which use bacteria/enzymes (e.g., enzymatic ring opening polymerization (eROP)). Besides PLA, also lactic acid (LA) synthesis is described and an emphasis is put on the biotechnological methods. Having regard to PLA copolymerization, this paper attempts to describe different types of PLA copolymers (such as block copolymers, PLA copolymers with polysaccharides, PLA-cellulose copolymer composites, and PLA polymer brushes). A detailed overview of the recent accomplishments in the field of PLA copolymers is presented. Various enhanced properties and applications of presented PLA copolymers are discussed. The attention is placed mainly on applications in the field of tissue engineering, drug delivery systems, and the packaging sector. Furthermore, a PLA market study and its economic forecast are presented. Eventually possible directions for future research in the field of PLA synthesis and copolymerization are indicated.
Ju Li, Lize Yang, Shuo Chen, Guotao Sun
Vol. 19., No.1., Pages 47-59, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.4
Vol. 19., No.1., Pages 47-59, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.4
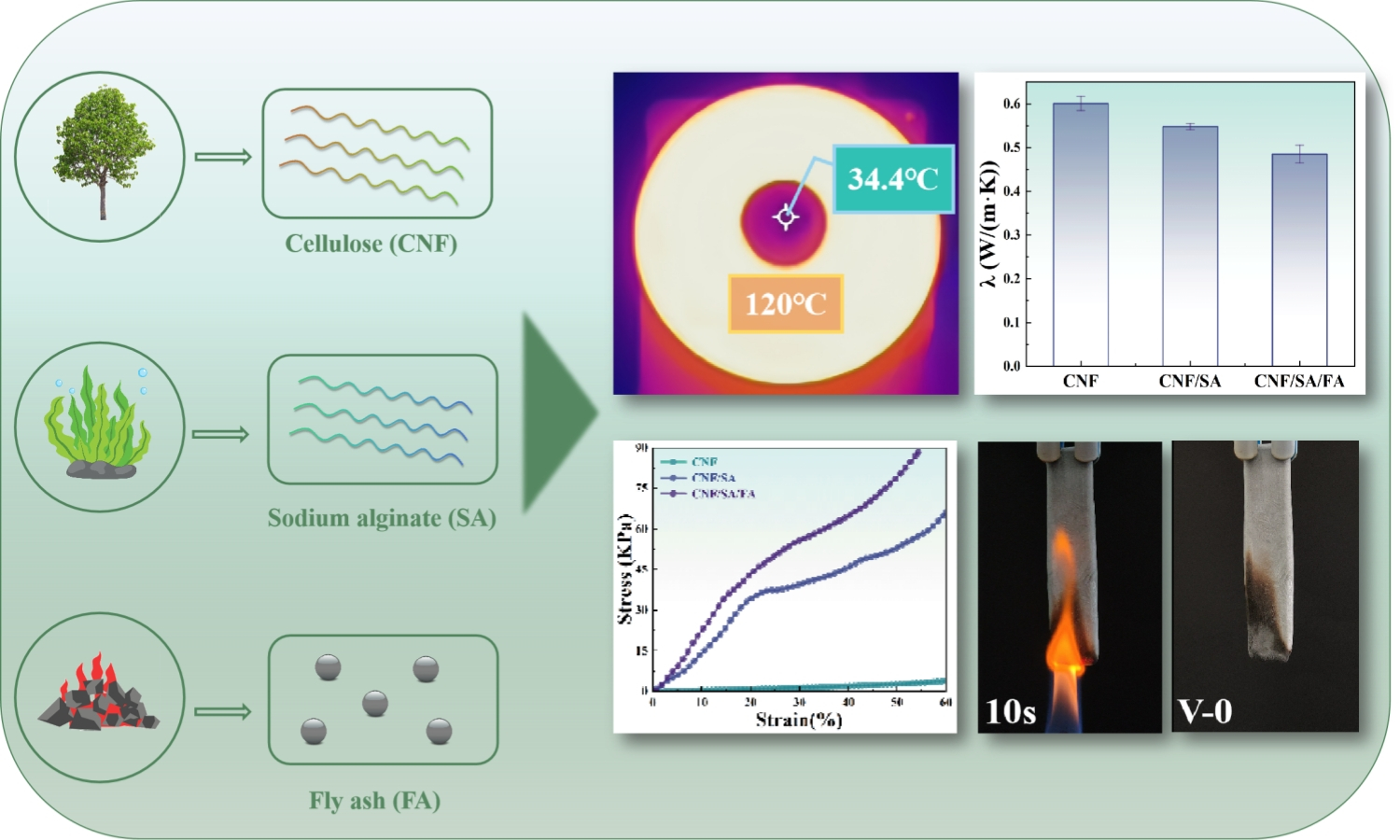
The widespread use of cellulose nanofiber (CNF)-based aerogels is hindered by their limited flame retardancy and mechanical properties. This study addresses these challenges by developing cellulose nanofiber/sodium alginate/fly ash (CNF/SA/FA) aerogel through a one-pot method, utilizing industrial waste fly ash (FA) as a reinforcing material. Various characterization and analytical techniques were employed to evaluate the properties of the CNF/SA/FA aerogel. The findings have revealed that resulting aerogel exhibited excellent thermal insulation performance, with a thermal conductivity of 0.485 W/(m·K), along with an impressive compressive strength of 88.4 kPa and favorable shape processability. Vertical combustion tests demonstrated a V-0 rating, indicating superior flame retardancy, and the aerogel achieved a remarkable 79.16% residual carbon, confirming their effective heat shielding capabilities. Notably, the incorporation of FA significantly enhanced both the thermal and mechanical properties of the composite aerogel, presenting a sustainable and effective solution to optimizing the properties of aerogel for thermal insulation.
Chin-San Wu, Shan-Shue Wang, Dung-Yi Wu, Wanwen Gu
Vol. 18., No.8., Pages 835-850, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.62
Vol. 18., No.8., Pages 835-850, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.62
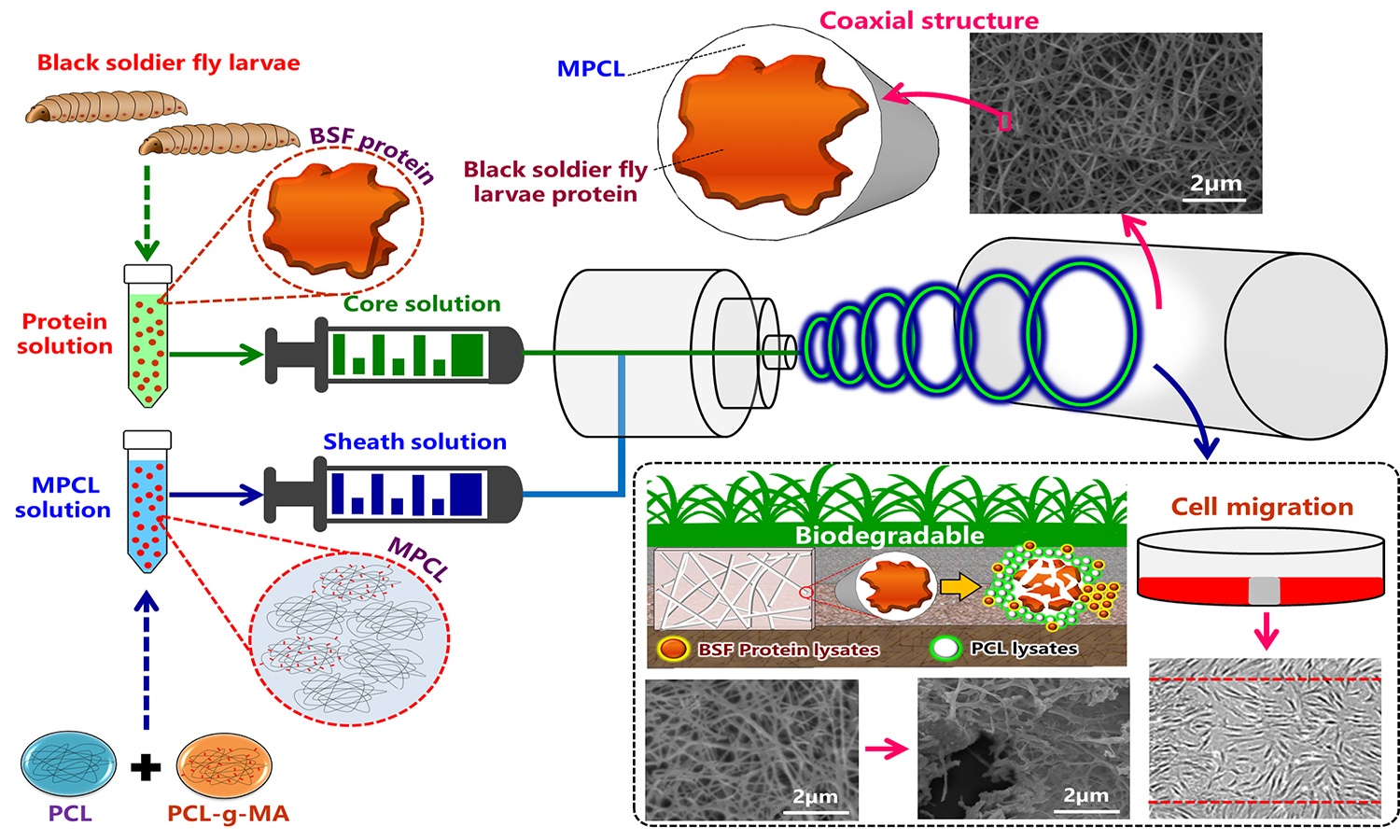
The protein from black soldier fly larvae was used as a functional ingredient of a novel green nanofiber. Larvae protein powder (LP) was blended with biodegradable poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) and processed in an electrospinning machine using a coaxial feeding/mixing method to produce nanofibers approximately 100–350 nm in diameter. To improve the dispersion and interface bonding of various PCL/LP nanofiber components, a homemade compatibilizer, maleic anhydridegrafted poly(ε-caprolactone) (MPCL), was added to form MPCL/LP nanofibers. The structure, morphology, mechanical properties, water absorption, cytocompatibility, wound healing, and biodegradability of PCL/LP and MPCL/LP nanofiber mats were investigated. The results showed enhanced adhesion in the MPCL/LP nanofiber mats compared to PCL/LP nanofiber mats; additionally, the MPCL/LP nanofibers exhibited increases of approximately 0.7–2.2 MPa in breaking strength and 9.0–22.8 MPa in Young’s modulus. Decomposition tests using a simulated body fluid revealed that the addition of LP enhanced the decomposition rate of both PCL/LP and MPCL/LP nanofiber mats and in vitro protein release. Cell proliferation and migration analysis indicated that PCL, MPCL, and their composites were biocompatible for fibroblast (FB) growth. Biodegradability was tested in a 30 day soil test. When the LP content was 20 wt%, the degradation rate exceeded 50%.




