Graphitic C3N4 incorporated chitosan-poly(vinyl alcohol) blend nanocomposites for the removal of Cu(II) and Cr(VI) ions from aqueous solutions
Shivapura Manchaiah Anush, Suchetha Naga Raju, Ballupet Honnapa Gayathri, Keresanthe Parameshwarappa Ajeya, Yarabahally Ravindranath Girish, Sanneerappa Darshan, Yelaware Puttaswamy Naveen, Kalappa Prashantha, Byrappa Krishnaiah Narendra, Aishwarya Jayaram
Vol. 18., No.1., Pages 102-115, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.8
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.8
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
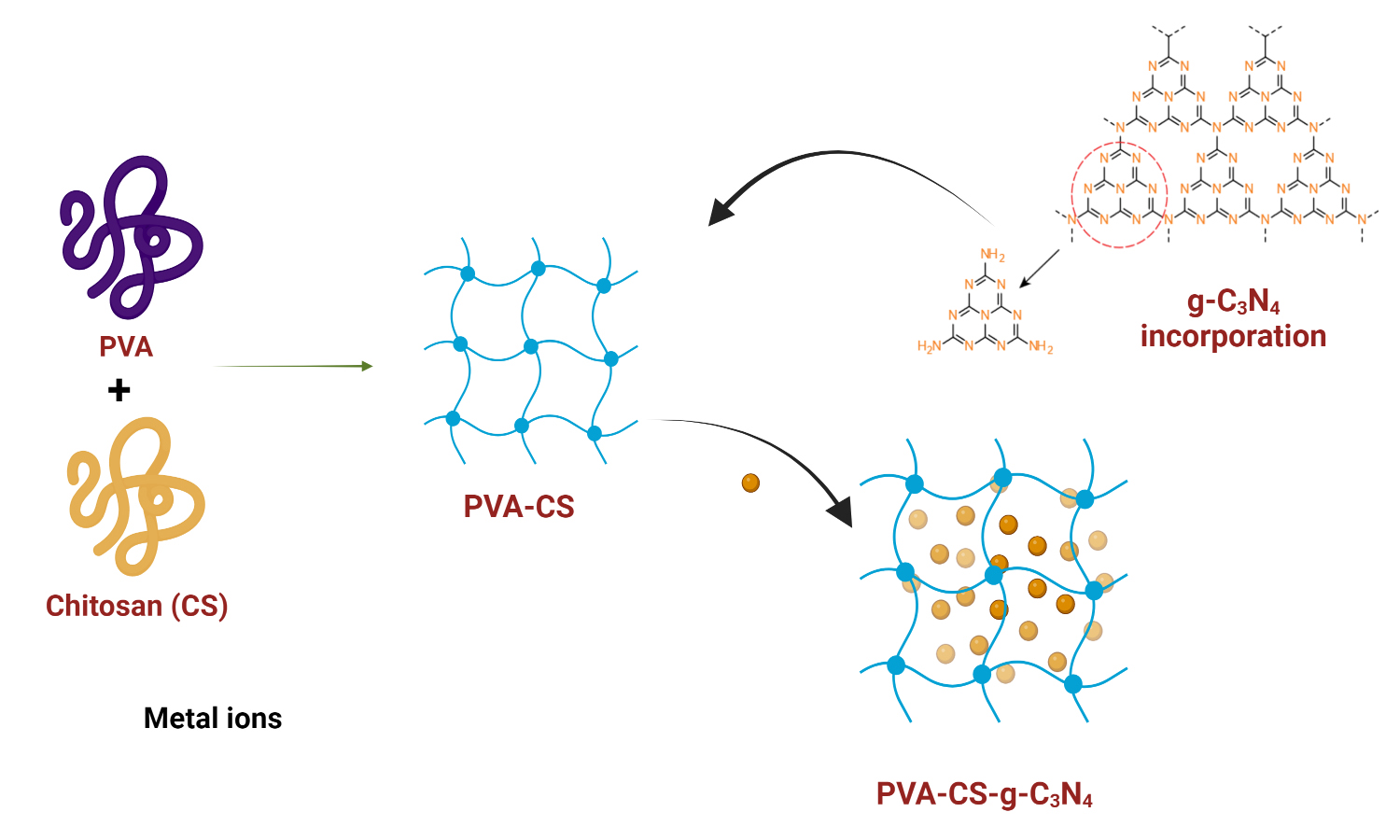
ABSTRACT
A novel adsorbent material for the effective removal of hazardous metal ions from aqueous solutions was developed through modifications to chitosan. The process involved the use of vanillin to create cross-linked chitosan, which was then combined with thiourea-based graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) to form a gel matrix. The resulting composite material was thoroughly characterized using various techniques, including Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and X-ray diffractometry. To assess its efficacy, adsorption experiments were conducted to determine the capability of the synthesized compounds to adsorb Cu(II) and Cr(VI) ions. The observed results found that the adsorption process was found to follow pseudo-second-order kinetics and the Langmuir isotherm model. Through thermodynamic studies, it was revealed that the adsorption process was both endothermic and spontaneous in nature. Furthermore, desorption studies confirmed that the material could be regenerated, making it reusable. This characteristic allowed for the effective recovery of the adsorbate species and highlighted the potential for reusing the adsorbent material multiple times.
RELATED ARTICLES
Xin Liu, Liang Xu, Yu Bai, Wei Wang, Zheng Li, Jizhou Du, Jing Zhang, Junfeng Qian, Mingyang He
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 292-310, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.23
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 292-310, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.23
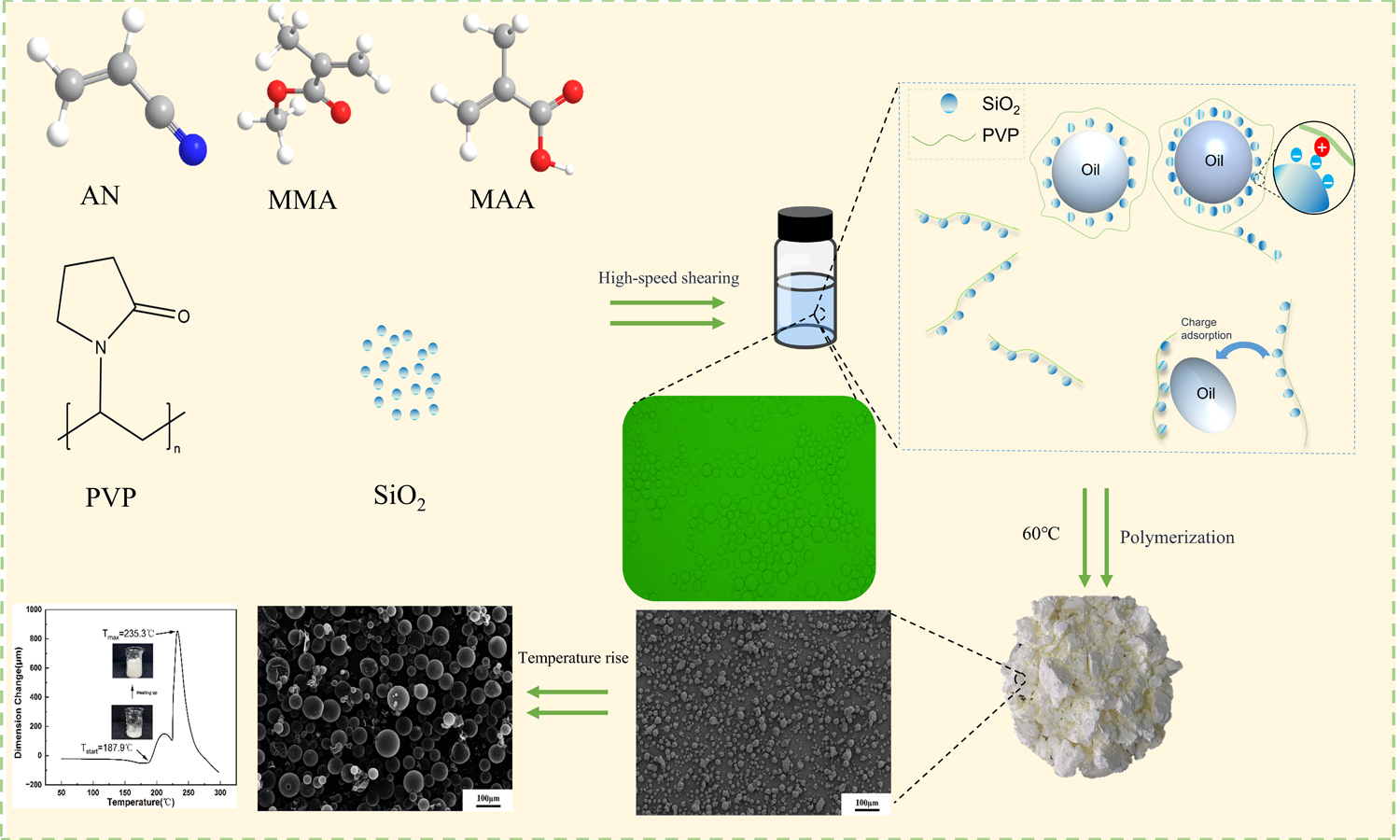
Thermally expandable microspheres (TEMs) are 5–50 μm core–shell particles that expand near the shell’s glass transition temperature (Tg). They are widely used as blowing agents in polymer foaming. Typically, TEMs are prepared by Pickering emulsion–based suspension polymerization. In this process, the oil phase contains monomers, a volatile blowing agent, and an initiator, and it is dispersed as oil-in-water droplets. The aqueous phase contains inorganic particles and an organic dispersant to stabilize the interface. However, solely regulating the oil phase has failed to deliver TEMs that couple a high onset expansion temperature (Tstart) with a large expansion ratio. Therefore, these materials remain unsuitable as blowing agents for high-processing-temperature polymers. This study systematically investigates how regulating the aqueous-phase environment affects Tstart and the expansion ratio of TEMs. Specifically, we tune silica concentration, pH, and ionic strength. By enhancing emulsion stability and optimizing emulsion morphology, we obtain TEMs that combine a high Tstart (188 °C) and a 12× diameter expansion. These findings highlight the importance of aqueous-phase regulation in controlling the Tstart and expansion ratio of TEMs, providing a promising route to microspheres suited for high-temperature polymer foaming.
Narayanapura Mahadevappa Tanuja, Sommenahalli Machegowda Chaithra, Chikkahalkur Shivanandappa Kaliprasad, Mangaravalli Hombalegowda Harshitha, Shivapura Manchaiah Anush, Kalappa Prashantha
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 36-51, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.4
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 36-51, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.4
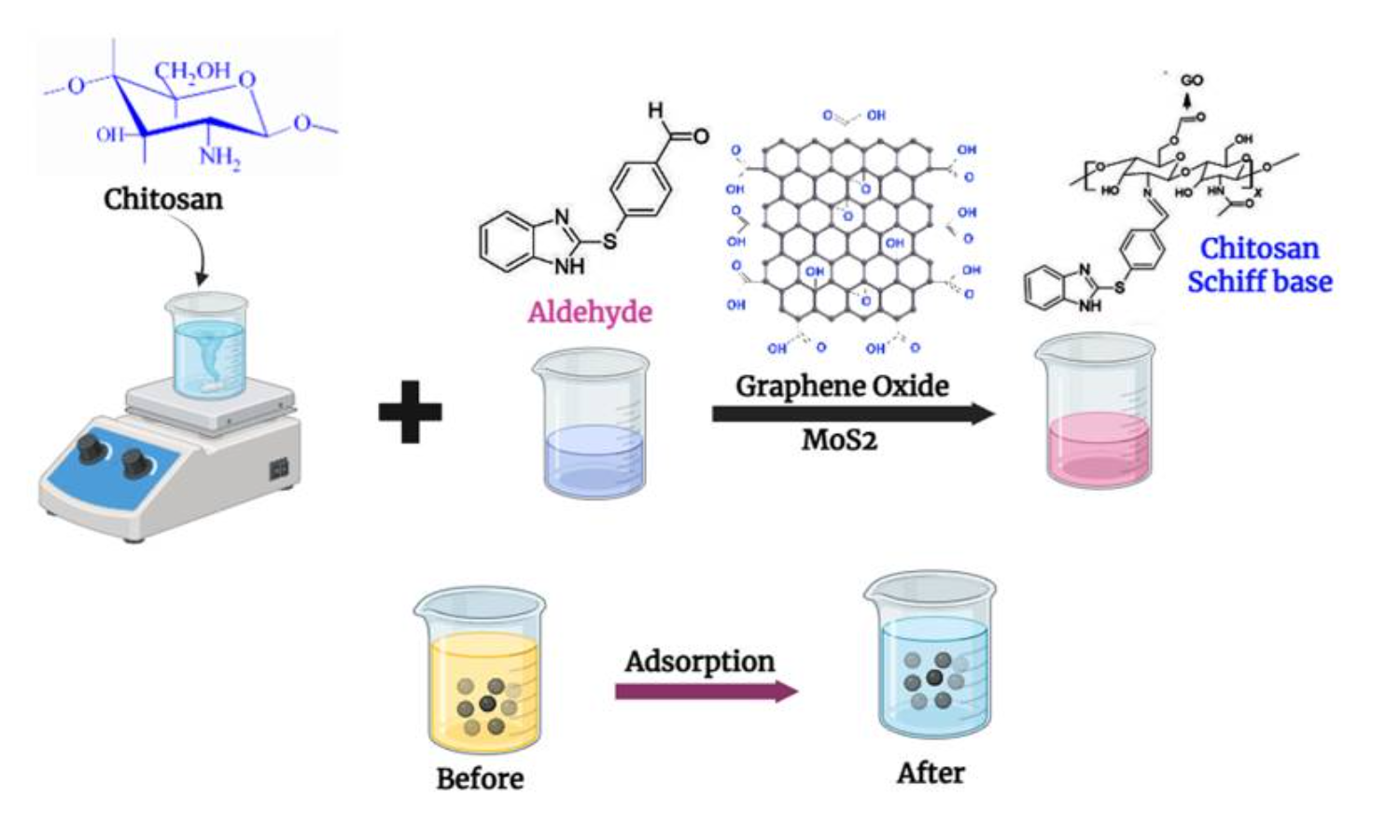
In this work, we have developed a novel absorbent material using chitosan (CS), and further it was structurally modified via reaction with thiocarbaldehyde, forming a Schiff base intermediate. Simultaneously, graphene oxide was functionalized at the C-6 position of CS through an effective esterification process and composited with the incorporation of molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanoparticles to synthesize a hybrid adsorbent material. The resulting material was characterized using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The synthesized adsorbent was subjected to the adsorptive removal of Cu(II) and Cr(VI) ions from dilute solutions. The maximum uptake of 66.66 mg/g for Cu(II) and 76.92 mg/g for Cr(VI) were recorded during the adsorption process, further following pseudo-second-order kinetics adsorptive nature and fitted well with the Langmuir isotherm model. Desorption studies indicated the material’s reusability, and the thermodynamic studies indicated a spontaneity with an endothermic adsorptive nature. These studies highlight the material’s potential as an effective adsorbent as a sustainable approach for efficient environmental remediation.
Mpho Phillip Motloung, Mokgaotsa Jonas Mochane
Vol. 19., No.11., Pages 1092-1132, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.82
Vol. 19., No.11., Pages 1092-1132, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.82

Polylactic acid (PLA) is one of the most widely used biopolymers, and it has demonstrated a huge potential for replacing some of the conventional plastics in certain application fields. However, due to a lack of other attributes such as antimicrobial properties and slow degradation rates, it is often blended with other polymers to impart these properties. Chitosan has desirable features including antimicrobial and antioxidant properties, biodegradability and biocompatibility, and environmental friendliness. Thus, it is widely blended with PLA to generate materials that can be applied in various fields. In recent years, PLA/chitosan blend composites and nanocomposites have been produced to develop sustainable and ecofriendly materials that can be suitable in active food packaging, water treatment, air filtration, and biomedical applications. This review provides an overview of the recent advancements in the development of PLA/chitosan blend composites and nanocomposites for various applications. The processing strategies, mechanical and thermal properties, together with utilization in biomedical, air filtration, water treatment, and packaging applications, are provided.



