Introducing metal-ligand coordination interaction for self-healing and recyclable nitrile–butadiene rubber: A facile strategy
Yuan Gao, Weiran Zhang, Junhao Wang, Zishuo Wang, Zhaobo Wang
Vol. 17., No.10., Pages 1019-1030, 2023
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2023.76
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2023.76
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
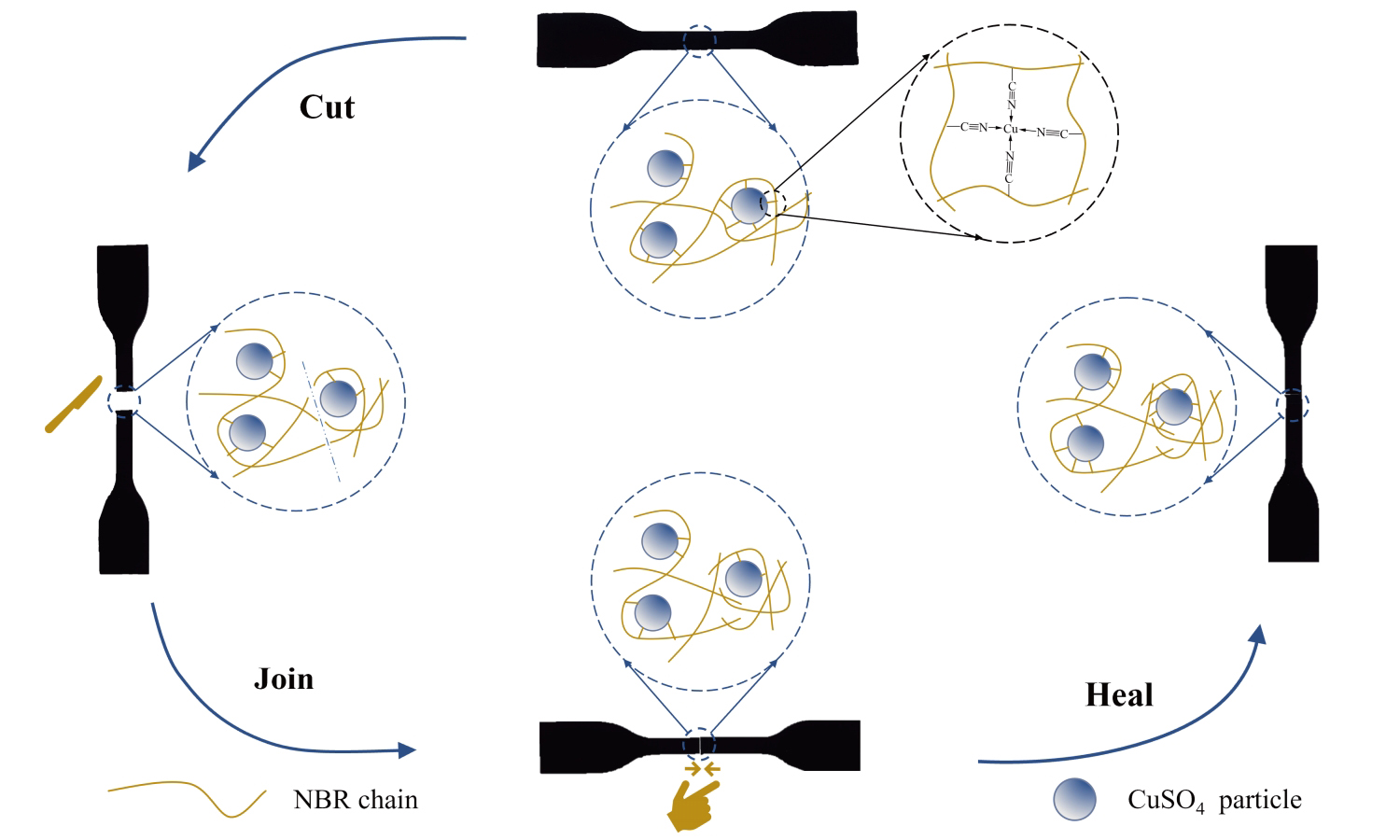
ABSTRACT
In this research, a nitrile-butadiene rubber (NBR) was prepared with excellent mechanical, self-healing and recycling properties by introducing metal-ligand coordination interaction. A coordination crosslinking network based on ligand bonding was successfully introduced in the NBR matrix by mechanical compounding. The dynamic reversibility of the coordination crosslinking network not only provides the vulcanizate with excellent mechanical properties but also confers a remarkable self-healing ability under high temperatures and recyclable property under mechanical shear, respectively. The sample, which was subjected to the complete cut, could be capable of restoring its original tensile strength after self-healing treatment. The self-healing efficiency of NBR vulcanizate is significantly dependent on the self-healing temperature and time, which can surprisingly reach 97% of the original tensile strength after self-healing treatment at 180 °C for 60 min. After the mechanical shear, the coordination crosslinking network is reversibly transformed. The tensile strength of the NBR vulcanizates after mechanical shearing recycling and re-vulcanization was similar to that of the original NBR vulcanizates. This research presents a novel approach to enhance the durability of rubber used in commercial applications, endowing it with reshaping and recycling capabilities and mitigating environmental issues associated with waste rubber.
RELATED ARTICLES
Rattanawadee Ninjan, Bencha Thongnuanchan, Phakawat Tongnuanchan, Subhan Salaeh, Jutharat Intapun, Abdulhakim Masa, Natinee Lopattananon
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 18-35, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.3
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 18-35, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.3
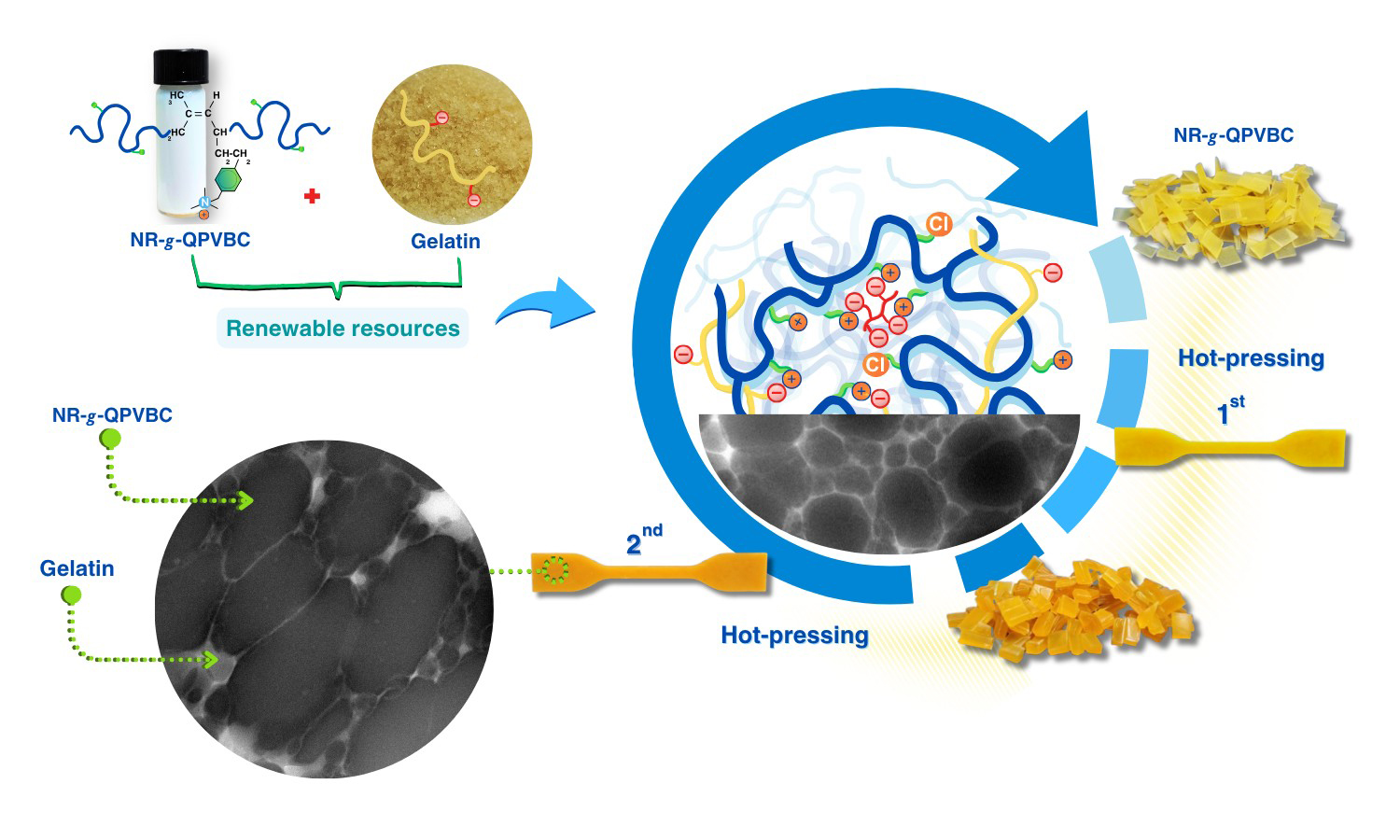
The present study has proposed a straightforward method to improve the reprocessability of modified natural rubber (NR) by blending it with gelatin (GT). The reprocessable characteristics of these blends were evaluated based on their remolding capabilities and mechanical recovery performance. In this method, poly(vinylbenzyl chloride) (PVBC) was first grafted onto NR chains to create graft copolymers known as NR-g-PVBC. The benzyl chloride groups in the graft copolymers were subsequently converted into quaternary ammonium groups, referred to as NR-g-QPVBC. This modification enabled ionic crosslinking when NR-g-QPVBC reacted with ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid. Blends were created by incorporating GT powder into the NR-g-QPVBC latex. The optimal loading level of GT was determined to be 30 wt%, as the resulting film exhibited the highest recovery of tensile properties. Initially, the film's tensile strength was measured at 15 MPa. After being remolded at 160 °C, the tensile strength decreased to 9.3 MPa, resulting in a recovery rate of 60.7% and withstanding a tensile strain of 144%. Although the NR-g-QPVBC/GT films could be remolded, their tensile properties declined with increasing remolding cycles. Therefore, this work demonstrated a practical method for producing NR-based films that could be reshaped through hot-pressing after being formed into products, increasing their reusability.
Liu Yang, Xuan Zhao, Sun Xinyu, Shuai Yuan, Lei Zhu
Vol. 19., No.8., Pages 783-795, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.60
Vol. 19., No.8., Pages 783-795, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.60
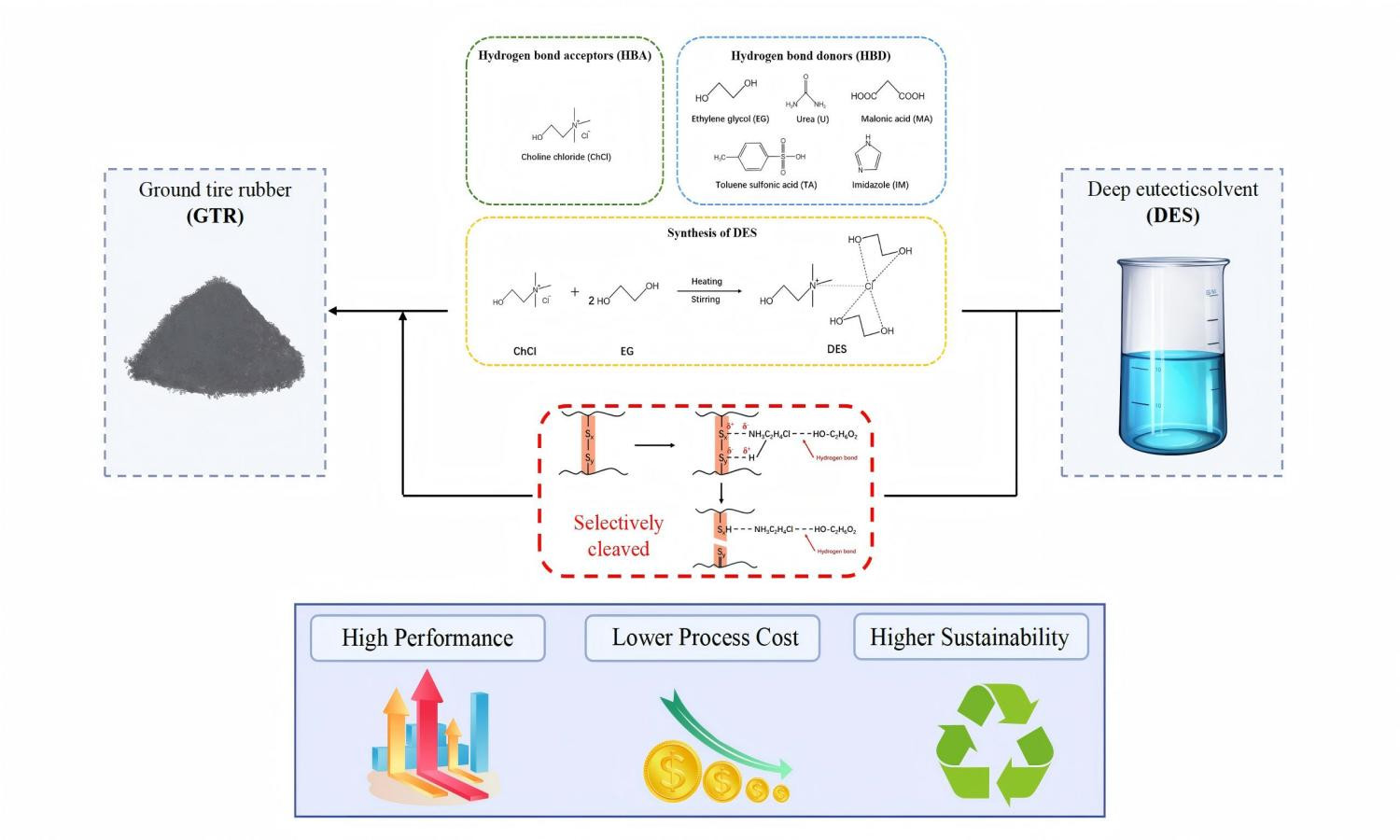
Waste tire rubber poses significant environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradability and complex crosslinkedvstructure. In this sense, this study aims to examine the utilization of deep eutectic solvents (DESs) in the desulfurizationvprocess of ground tire rubber (GTR). A range of hydrogen bond donors (HBDs), including ethylene glycol, malonic acid,vimidazole, toluene sulfonic acid, and urea, were combined with choline chloride, which serves as a hydrogen bond acceptorv(HBA), to synthesize deep eutectic solvents. Subsequently, these DESs are used in the modification of rubber devulcanizationvprocesses. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and Horikx analysis werevused to confirm the occurrence of devulcanization. The studies confirmed that the devulcanization process was selective invnature, effectively reducing random chain scission while maintaining the integrity of the polymer. Furthermore, the vulcanizatesvobtained post-treatment demonstrated enhanced properties, including increased tensile strength, modulus, tear strength, hardness, and durability, with ethylene glycol-based DES (DES-E) exhibiting the most pronounced enhancements.
Cristian Valdés, Valentina Guzmán, Camila Ponce, Maribel Mamani, Juan Guevara, Claudia Vergara, Rodrigo Andler
Vol. 19., No.6., Pages 594-609, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.45
Vol. 19., No.6., Pages 594-609, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.45
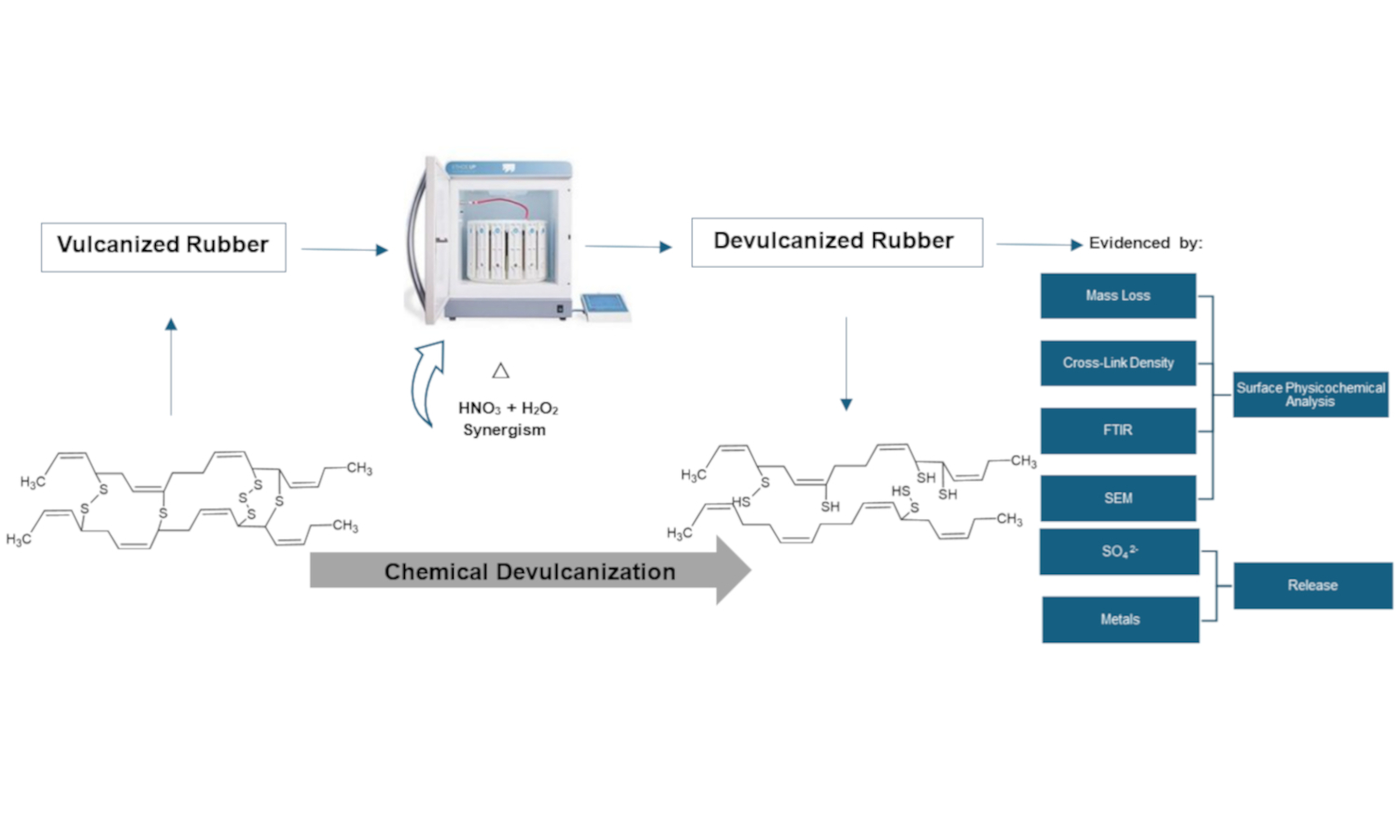
Waste rubber disposal causes considerable negative environmental impacts due to its increase worldwide, mainly in the automotive industry. Therefore, the search for technological solutions for rubber waste is a priority, and the first step in this material degradation is devulcanization due to its difficult degradation. This study evaluated rubber devulcanization using a closed vessel microwave digestion system with nitric acid (HNO3) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) through chemical characterization, aiming at verifying the synergistic effect between these oxidizing agents. Microwave irradiation was applied as a heating method to facilitate the chemical reactions, focusing on the synergism between HNO3 and H2O2. Results showed that 5 M H2O2 in combination with 1% HNO3, presented better results. A greater decrease in cross-link density was demonstrated as the concentration of H2O2 increased (3.96·10–5±1.99·10–6 mol/cm3), likewise, higher sulfates released (926.8±53.4 mg/L), increased mass loss (12.184±1.06%), rubber surface fragmentation, and important variations in the C–S, C=O bands, showing better results when devulcanization is carried out in synergism between HNO3 and H2O2.
Shengao Yang, Yan Wang, Fang Wang, Kaiyi Zhang, Xinxin Lv, Hao Teng, Rui Zheng, Faliang Luo, Qian Xing
Vol. 19., No.1., Pages 94-106, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.7
Vol. 19., No.1., Pages 94-106, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.7
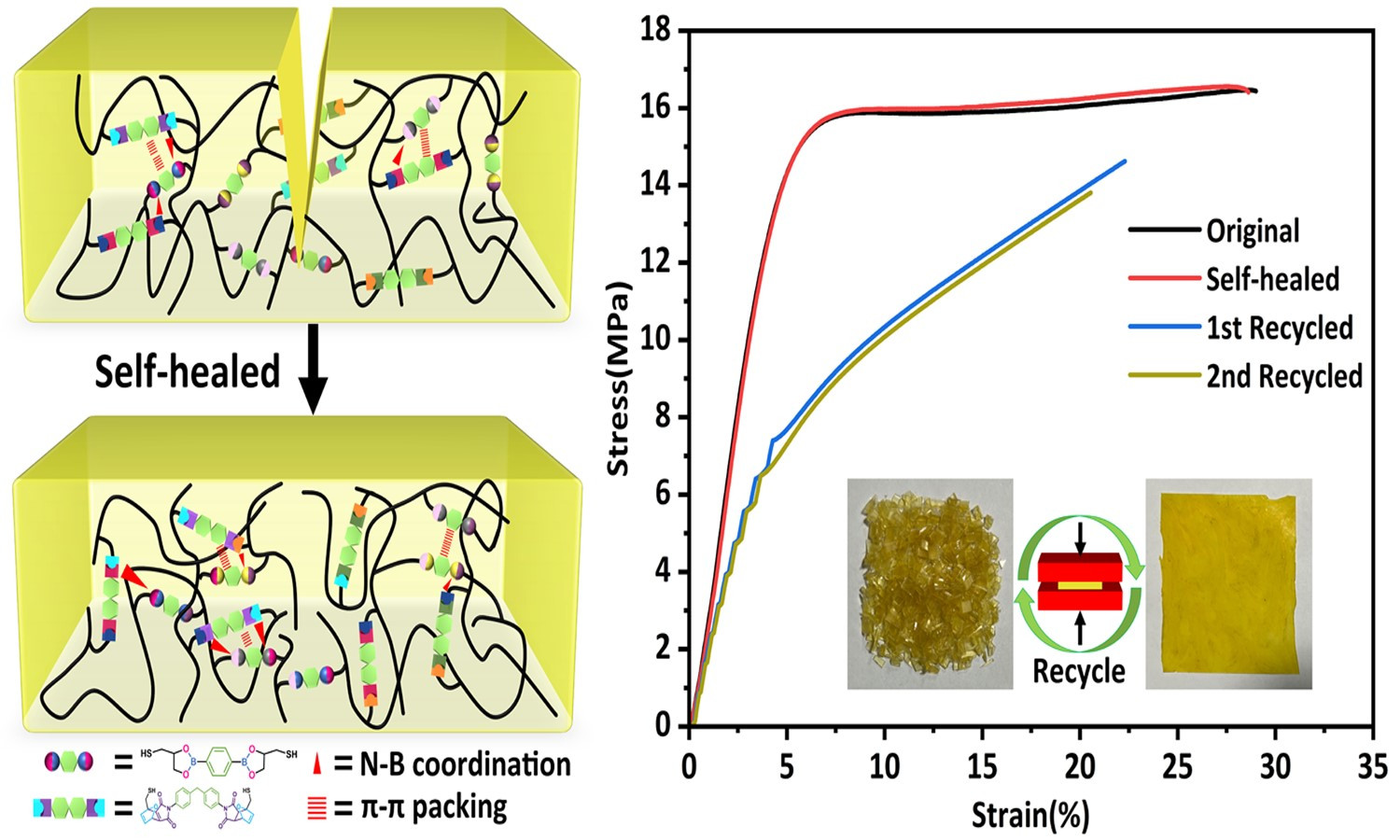
Dynamic cross-linked networks (DCNs) endow thermoset rubber with self-healability and recyclability to extend its lifetime and alleviate environmental pollution. However, the contradiction between high self-healing and mechanical properties in DCNs rubber is always difficult to be resolved. Herein, we used boronic ester (BO) and Diels-Alder dynamic covalent bonds (DA) to synthesize polybutadiene-based dual networks rubber (PB-BO-DA) via thiol-ene reaction. This approach achieved a tensile strength of 16.46 MPa and 99% self-healing efficiency, facilitated by extensive intermolecular interactions (π-π packing and N-B coordination) and fully dynamic cross-linking. In addition, multiple dynamic cross-linked networks (MDCNs) polybutadiene-based rubber also show excellent shape memory ability and recyclability. This strategy might open a helpful pathway to fabricate intelligent multifunctional polymers with high strength and high self-healing efficiency.
Agata Rodak, Józef Haponiuk, Shifeng Wang, Krzysztof Formela
Vol. 18., No.12., Pages 1191-1208, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.91
Vol. 18., No.12., Pages 1191-1208, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.91
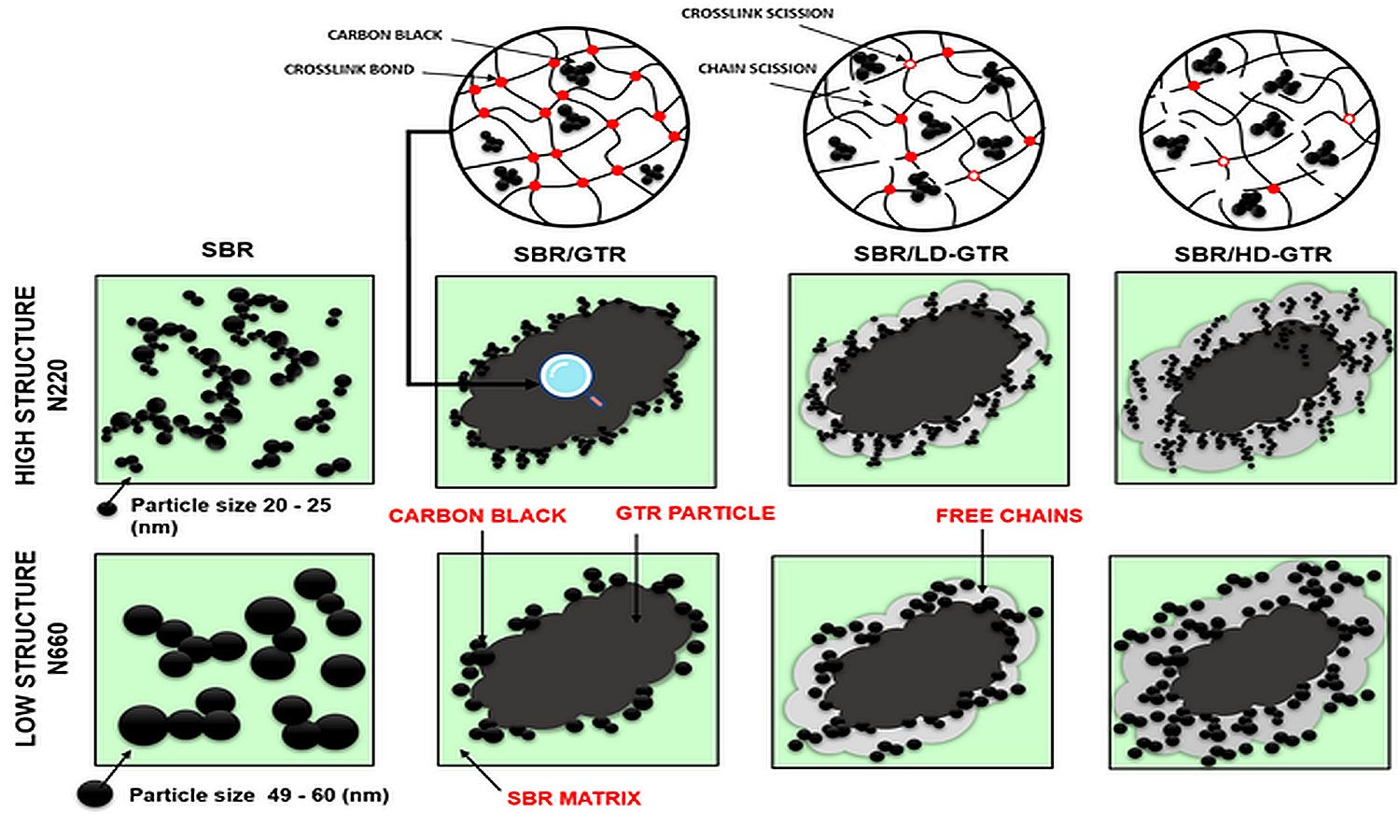
Carbon black migration between ground tire rubber (GTR) and rubber matrix is essential in developing high-performance rubber/GTR composites. In this work, carbon black N220 (surface area: 107.1 m2/g, particle size: 20–25 nm) and N660 (surface area: 33.1 m2/g, particle size: 49–60 nm) were used as the reinforcement fillers for styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) blended with reclaimed GTR. The combined effects of GTR devulcanization level and carbon black grade on the properties of SBR/GTR composites were investigated considering curing characteristics, thermal stability, physico-mechanical properties, dynamic mechanical properties, swelling behavior, and morphology. The results showed that, regardless of GTR devulcanization level and carbon black grade, application of GTR resulted in deterioration of mechanical properties compared to a reference sample without GTR. It was observed the reinforcement effect of carbon black in SBR/GTR composites was more visible with higher devulcanization level of GTR and lower particle sizes of carbon black fillers. SBR/GTR composites reinforced with carbon black N220 were characterized by tensile strength in the range of 15.3–16.3 MPa and abrasion resistance in the range of 120–123 mm3, which justify their potential application in the manufacturing of technical rubber goods or footwear.



